Exploring DAG Technology in Blockchain: A New Frontier


Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) Technology in Cryptocurrency
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) technology has emerged as a potential alternative to blockchain in the cryptocurrency space. This article explores the concept of DAG, its workings, and how it compares to blockchain technology.
DAG vs blockchain technology
DAG is a data modeling tool used by some cryptocurrencies instead of a blockchain. While blockchain technology remains dominant in the crypto industry, DAG has been considered a potential disruptor due to its advantages.
DAG architecture
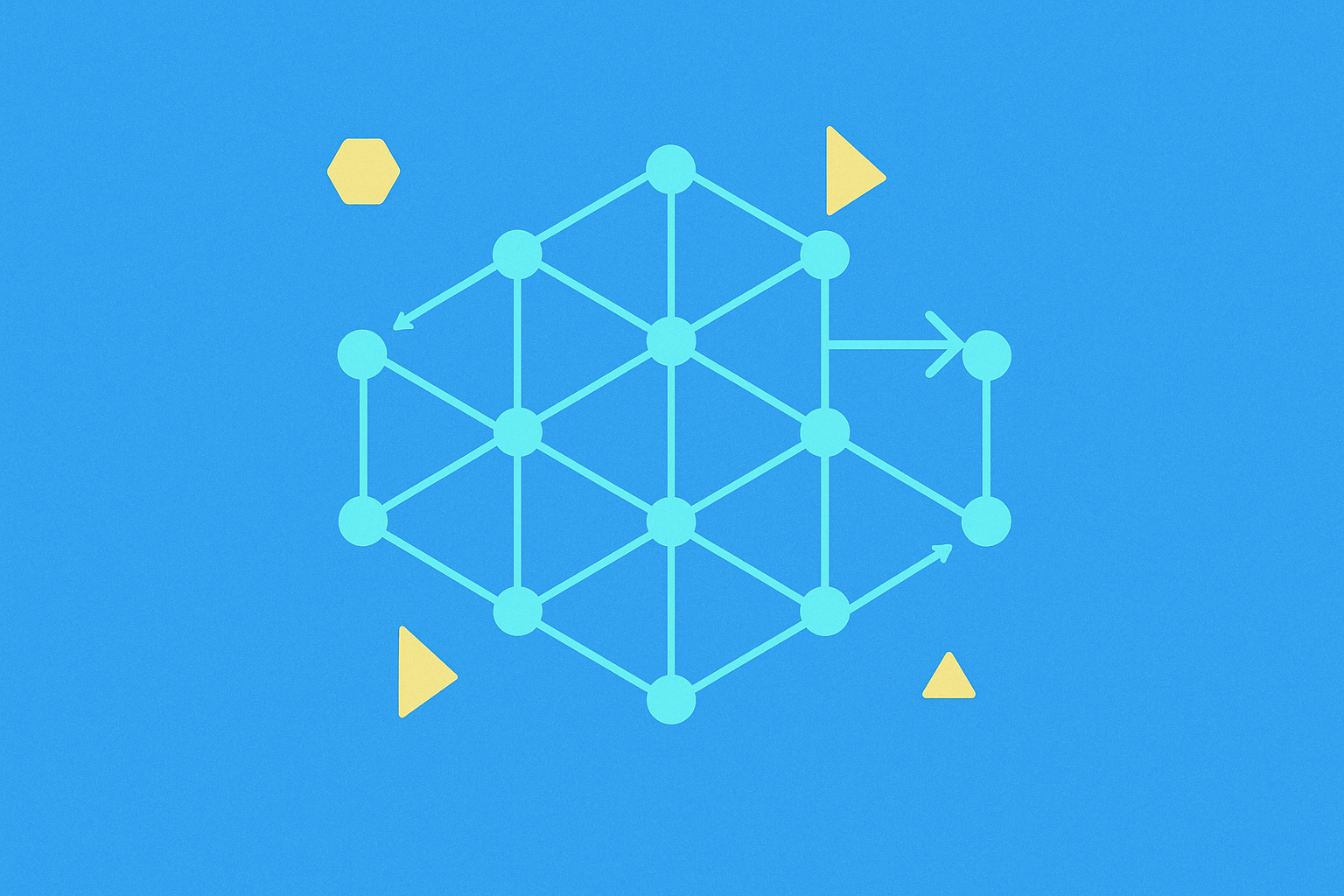
The DAG architecture is based on circles (vertices) and lines (edges). Vertices represent activities to be added to the network, while edges show the order of transaction approval. This structure allows for efficient data modeling and consensus achievement in distributed networks.
What's the difference between a DAG and a blockchain?
Unlike blockchains, DAGs don't create blocks. Instead, they build transactions on top of previous ones. Visually, blockchains appear as chains of blocks, while DAGs resemble graphs with circles and lines.
How does DAG technology work?
In a DAG system, users must confirm a previous transaction (tip) before submitting their own. This process creates layers of transactions, allowing the system to grow continuously. DAG also incorporates a mechanism to prevent double-spending by assessing the entire transaction path.
What is DAG used for?
DAG technology is primarily used for processing transactions more efficiently than blockchain. It offers faster transaction speeds, energy efficiency, and the ability to handle micropayments with minimal or no fees.
Which cryptocurrencies use DAG?
Several cryptocurrencies have adopted DAG technology, including:
- IOTA (MIOTA): Known for its fast transactions, scalability, and security.
- Nano: Combines DAG and blockchain technology for quick, fee-less transactions.
- BlockDAG: Offers energy-efficient mining with more frequent halving events.
DAG pros and cons
DAG technology presents several advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- Faster transaction speeds
- Zero or minimal fees
- Energy efficiency
- Improved scalability
Cons:
- Potential decentralization issues
- Limited real-world testing at scale
Conclusion
Directed Acyclic Graph technology shows promise in addressing some of the limitations of blockchain, particularly in terms of transaction speed, fees, and scalability. However, it is still a relatively young technology with unexplored potential and limitations. While DAG may not entirely replace blockchain, it offers an intriguing alternative for certain cryptocurrency projects. As the technology evolves, it will be interesting to see how DAG develops and what new use cases emerge in the ever-changing landscape of cryptocurrency and distributed ledger technologies.
FAQ
What does DAG stand for?
DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph, a data structure used in blockchain technology for faster and more scalable transactions.
What is a DAG slang?
DAG in crypto refers to Directed Acyclic Graph, a data structure used by some blockchain alternatives for faster, more scalable transactions.
What is DAG?
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a data structure used in cryptocurrencies to improve scalability and transaction speed. It allows for parallel processing of transactions, unlike traditional blockchain.
What does DAG mean in America?
In America, DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph, a data structure used in computer science and blockchain technology. It represents a network of nodes without cycles, often used for efficient data processing and consensus mechanisms.

Exploring the Polkadot Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Guide to Blockchain Innovation

How to Measure Crypto Community Engagement: Key Metrics Revealed

Exploring Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology

Exploring Directed Acyclic Graph Technology in Blockchain Systems

Exploring The Benefits of DAG Technology in Blockchain Systems
Polymarket: A Decentralized Prediction Market Platform

Leading Web3 Wallet Launches K-NFT Week to Strengthen Presence in Asian Markets

Buy U.S. Stocks with Crypto: How to Use xStock Feature in Web3 Wallets

Social Metaverse Launchpad: Daoversal Subscription Launching Soon

What Is Goggles (GOGLZ)? Exploring the Meme-Powered Token on Sonic Blockchain
