Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology

What is a directed acyclic graph (DAG)?
Directed acyclic graph (DAG) is an innovative technology in the cryptocurrency space that offers an alternative to traditional blockchain technology. This article explores the concept of DAG, its workings, and how it compares to blockchain technology.
DAG vs blockchain technology
DAG is a data modeling tool used by some cryptocurrencies instead of a blockchain. While blockchain technology structures data in a chain of blocks, DAG uses a system of circles (vertices) and lines (edges) to represent and connect transactions. This unique structure allows for faster transaction processing and improved scalability compared to traditional blockchain systems.
How does DAG technology work?
In a DAG-based system, each transaction (represented by a circle or vertex) is built on top of previous transactions. To make a new transaction, a user must first confirm one or more previous unconfirmed transactions, known as "tips." This creates a layered structure of interconnected transactions, eliminating the need for block creation and mining.
DAG technology also incorporates a system to prevent double-spending. When confirming transactions, nodes assess the entire transaction path back to the first transaction, ensuring the balance is sufficient and all previous transactions are valid.
What is DAG used for?
DAG technology is primarily used for processing transactions more efficiently than blockchain. Its key applications include:
- Fast transaction processing: Without the need for block creation, DAG allows for quicker transaction confirmations.
- Energy-efficient operations: DAG systems consume less energy compared to proof-of-work blockchain networks.
- Micropayments: DAG's low or zero transaction fees make it ideal for small value transactions.
- Improved scalability: The absence of block times allows DAG to handle a higher volume of transactions.
Which cryptocurrencies use DAG?
Several cryptocurrency projects have adopted DAG technology, including:
- IOTA (MIOTA): A project focused on Internet of Things applications, known for its fast transaction speeds and scalability.
- Nano: A hybrid project combining DAG and blockchain technology, offering fast transactions with zero fees.
- BlockDAG: A project that uses DAG technology for energy-efficient mining.
DAG pros and cons
DAG technology offers several advantages:
- Faster transaction speeds
- Low or zero transaction fees
- Energy efficiency
- Improved scalability
However, it also faces some challenges:
- Potential centralization issues
- Limited testing at scale
- Less widespread adoption compared to blockchain technology
Conclusion
Directed acyclic graph (DAG) technology presents an intriguing alternative to traditional blockchain systems, offering potential improvements in transaction speed, scalability, and energy efficiency. While DAG has shown promise in addressing some limitations of blockchain technology, it is still in its early stages of development and adoption. As the technology continues to evolve, it remains to be seen how DAG will compare to other blockchain solutions and whether it can overcome its current limitations to become a more widely adopted solution in the cryptocurrency space.
FAQ
What is DAG used for?
DAG is used for organizing and optimizing data workflows, representing task dependencies, and ensuring efficient execution of complex processes in distributed systems and blockchain networks.
What is the difference between a directed acyclic graph and a directed graph?
A directed graph can have cycles, while a directed acyclic graph (DAG) cannot. DAGs have directed edges but no loops.
How do you determine if a graph is a DAG?
Check for no cycles and directed edges. Verify a valid topological ordering or successful sorting without errors.
How to interpret a directed acyclic graph?
A DAG consists of nodes and directed edges, representing tasks and dependencies without cycles. Nodes signify data points or tasks, while edges show directional flow between them.

Guide to Engaging in Parachain Auctions on Polkadot

Understanding Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)

Mastering the Fundamentals of Directed Acyclic Graphs

Exploring the Potential of Internet Computer Protocol (ICP)

Introduction to Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG)
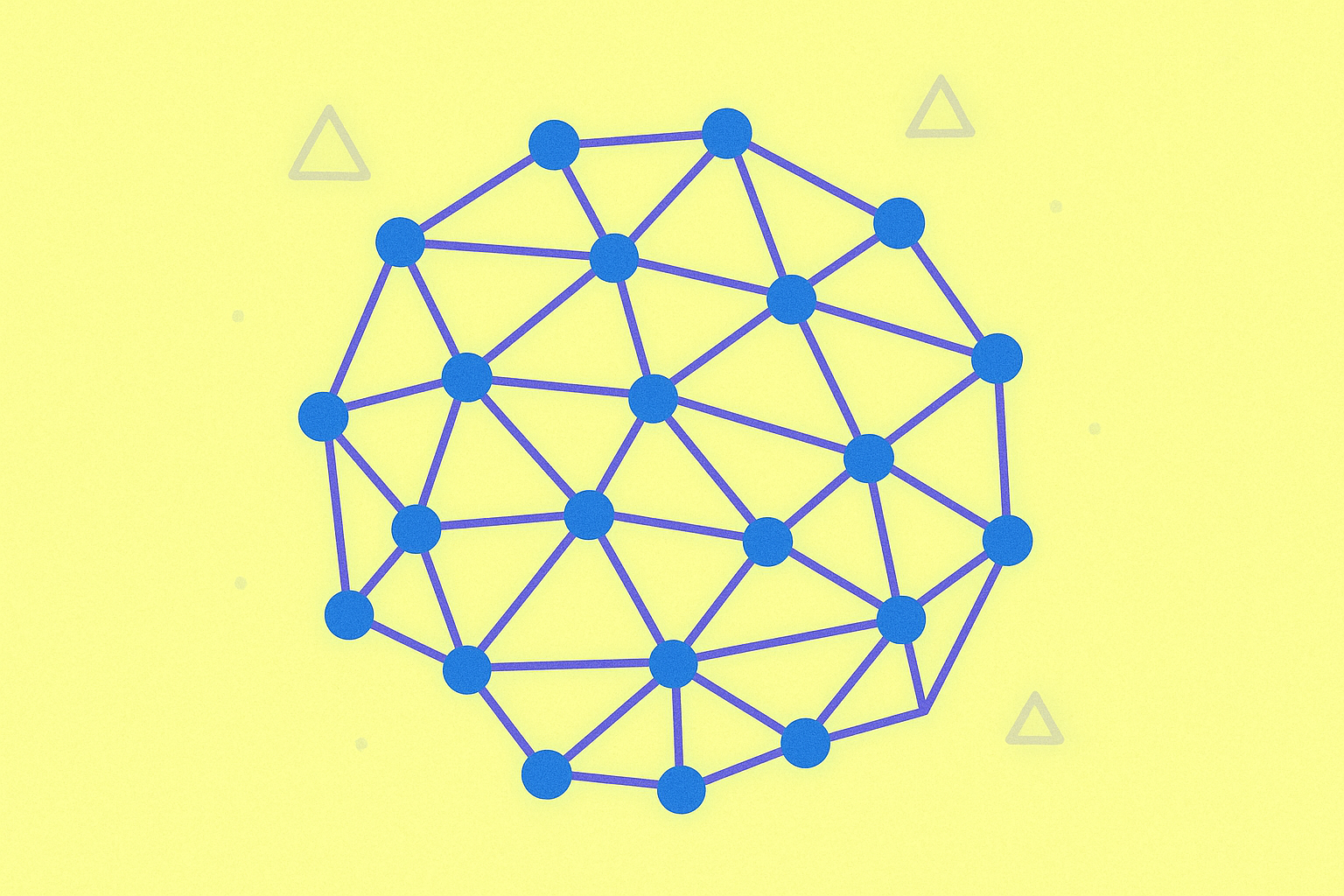
Exploring Distributed Ledgers: A Non-Block Approach

Understanding Decentralized Exchanges and DEX Aggregators
DEX Aggregator Platform Upgrade: Enhanced Trading Experience

Comprehensive Multi-Chain NFT Marketplace

What Is Monad? How to Claim Monad (MON) Tokens Using the Web3 Faucet

Grok AI Adoption: Ushering in a New Era for Blockchain Applications
