
What Does a Fake Bitcoin Look Like?

What Really Is a Fake Bitcoin in Crypto?
A rising concern for new crypto users is understanding what a fake bitcoin looks like and how to identify fraudulent digital assets. In the cryptocurrency space, a "fake Bitcoin" generally refers to counterfeit digital assets, misleading representations, or fraudulent schemes pretending to be the original Bitcoin (BTC).
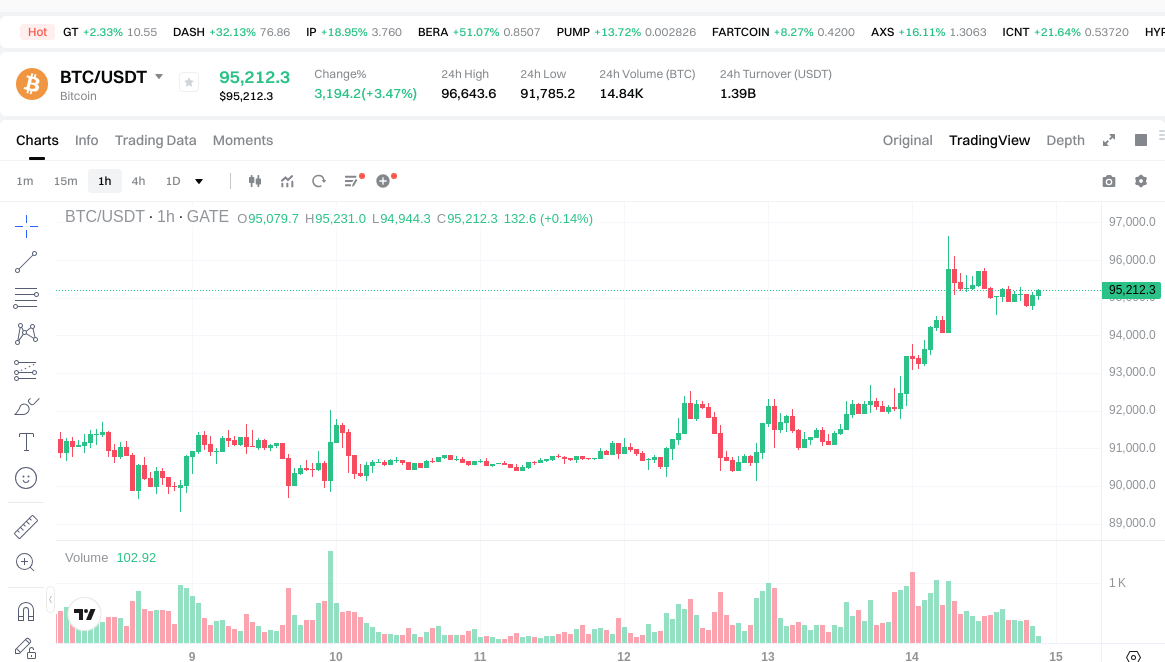 These scams manifest in various forms, from imposter tokens and phishing websites to fake payment confirmations and physical collectibles marketed as genuine cryptocurrency.
These scams manifest in various forms, from imposter tokens and phishing websites to fake payment confirmations and physical collectibles marketed as genuine cryptocurrency.
The financial impact of such fraud is substantial. According to comprehensive reports from Chainalysis and the FBI, fake Bitcoin scams cost the global crypto community millions of dollars each year, with losses continuing to escalate as scammers develop increasingly sophisticated tactics. Understanding what a fake Bitcoin looks like—and how to avoid falling victim—is crucial for anyone exploring digital assets, whether you're a first-time buyer or an experienced trader looking to protect your portfolio.
The challenge lies in the fact that Bitcoin, being entirely digital and decentralized, creates opportunities for bad actors to exploit newcomers' lack of technical knowledge. Unlike traditional financial fraud that might involve counterfeit bills or forged checks, fake Bitcoin scams operate in the digital realm where verification requires understanding blockchain technology and recognizing red flags that may not be immediately obvious to untrained eyes.
Common Signs of Fake Bitcoin and Scams
Recognizing fake Bitcoins involves more than just examining wallet addresses or transaction hashes. It requires a comprehensive understanding of how legitimate Bitcoin operates and where scammers typically exploit vulnerabilities. Here are the most common red flags that should immediately raise concerns:
Unverified Exchanges: Scammers frequently promote unofficial websites or mobile applications claiming to sell Bitcoin at unusually attractive rates or with "exclusive" features. Unlike legitimate operators that maintain transparent regulatory compliance and undergo regular security audits, these fraudulent platforms often lack clear regulatory data, provide minimal transparency about their operations, and typically disappear once users deposit funds. Warning signs include domains registered recently, missing contact information, absence of regulatory licenses, and promises of returns that seem too good to be true. These platforms may also pressure users to act quickly, claiming limited-time offers to prevent careful research.
Physical Bitcoins: In the purely digital world of cryptocurrency, Bitcoin has no physical form whatsoever. "Bitcoin coins" or attractive metallic tokens offered on online marketplaces, social media platforms, or novelty shops are simply collectibles with no actual blockchain value. No physical object can function as Bitcoin except as a decorative display item, and they hold absolutely no real value on the blockchain network. Some legitimate companies have created physical Bitcoin collectibles with embedded private keys, but these are clearly marketed as collectibles and require careful verification—most "physical Bitcoins" sold online are simply worthless novelties designed to deceive uninformed buyers.
Imposter Tokens: Some fraudulent projects launch copycat tokens with names or ticker symbols intentionally similar to Bitcoin to confuse potential buyers. These assets exist outside the main Bitcoin network and provide zero utility, recognition, or connection to the actual Bitcoin blockchain. For example, tokens named "BitcoinsX," "BTC Plus," "Bitcoin Cash Gold," or similar variants are not connected to genuine Bitcoin (BTC). They may be listed on obscure exchanges or promoted through social media with false claims about being "improved versions" or "the next Bitcoin." The only legitimate Bitcoin uses the ticker symbol BTC or ₿ and operates on the Bitcoin mainnet.
Fake Payment Confirmations: Fraudsters may generate convincing screenshots or fabricated transaction receipts to convince sellers they've received Bitcoin payments when no actual blockchain transaction occurred. These fake confirmations might include realistic-looking transaction IDs, timestamps, and wallet addresses. However, authenticity can only be verified on the official Bitcoin blockchain using public explorers like Blockchain.com or Blockchair. Real Bitcoin transactions are permanently recorded on the blockchain and can be independently verified by anyone, whereas fake confirmations exist only as manipulated images or documents.
| Characteristic | Real Bitcoin | Fake Bitcoin Scams |
|---|---|---|
| Symbol | BTC or ₿ | BTX, BTC2, BTCX, or similar variants |
| Form | Purely digital on blockchain | Physical coins, tokens, or trophies |
| Blockchain | Bitcoin Mainnet (public ledger) | Private chains, no blockchain, or alternative networks |
| Purchase Source | Trusted regulated exchanges | Social media offers, unknown websites, unsolicited messages |
| Verification | Public blockchain explorers | Screenshots, edited receipts, or unverifiable claims |
| Transaction Speed | 10-60 minutes for confirmations | Instant or suspiciously fast "confirmations" |
| Price | Market rate across major exchanges | Significantly below or above market rate |
Popular Fake Bitcoin Schemes and Their Impact
The cryptocurrency fraud landscape continues to evolve, with scammers developing increasingly sophisticated methods to deceive users. Understanding the most widespread forms of fake Bitcoin activity can help you recognize and avoid these schemes:
Phishing Scams: These involve fraudulent emails, text messages, or social media communications directing users to fake wallet providers or exchange websites that closely mimic legitimate platforms. The fake sites are designed to harvest login credentials, private keys, or seed phrases. Unsuspecting users may unknowingly reveal their sensitive information or send Bitcoin to non-existent addresses controlled by scammers. Advanced phishing attempts now use SSL certificates and professional designs that make them nearly indistinguishable from legitimate sites to untrained eyes. Some phishing campaigns even use compromised email accounts of real users to add credibility to their fraudulent messages.
Ponzi and High-Yield Schemes: These platforms promise guaranteed, outsized returns based on supposed "Bitcoin trading algorithms," "AI-powered mining packages," or "exclusive investment opportunities." They typically require upfront investments and may initially pay returns using new investors' money to create the illusion of legitimacy. These schemes almost always collapse when new investment slows, leaving the majority of investors without funds. Warning signs include guaranteed returns (no legitimate investment can guarantee profits), pressure to recruit others, complex or vague explanations of how profits are generated, and withdrawal restrictions or delays.
Impersonation Scams: Fraudsters create fake profiles pretending to be cryptocurrency influencers, exchange support agents, celebrities, or successful traders. They may request Bitcoin for supposed giveaways, promotions, investment opportunities, or to "verify" accounts. These scams often use hijacked verified social media accounts or create convincing duplicates with slightly altered usernames. They may also use deepfake technology or edited videos to add credibility. Legitimate companies and individuals never request cryptocurrency payments for giveaways or support services.
Fake Wallet Applications: Some mobile applications available through unofficial app stores or direct downloads pretend to be Bitcoin wallets, but in reality, they harvest user credentials, private keys, and seed phrases. These malicious apps may appear functional, showing fake balances and transaction histories, while secretly transmitting user data to scammers. Always download wallet applications only from official sources and use established wallet solutions with proven security track records and regular independent audits.
According to comprehensive research by Chainalysis, over $7.7 billion was lost to cryptocurrency scams in 2021 alone, with fake Bitcoin transactions representing a significant proportion of these losses. More recent data suggests these numbers have continued to grow, with scammers becoming more sophisticated in their approaches and targeting users across all experience levels. The average loss per victim has also increased, indicating that scammers are successfully targeting higher-value transactions and more experienced users who might have previously considered themselves immune to such fraud.
How to Protect Yourself Against Fake Bitcoin
Protection against fake Bitcoin requires a multi-layered approach combining technical verification, platform selection, and security best practices. Both beginners and experienced users can implement these essential steps to verify the authenticity of Bitcoin transactions and avoid scams:
Use Trusted Platforms: Choose regulated and reputable exchanges with established track records, transparent operations, and proper licensing for all your cryptocurrency purchases. Research platforms thoroughly before creating accounts, checking for regulatory compliance, user reviews from multiple sources, security certifications, and operational history. Mainstream exchanges implement rigorous security measures including cold storage for user funds, insurance policies, regular security audits, and multi-factor authentication requirements. Avoid platforms promoted through unsolicited messages, those offering prices significantly different from market rates, or those lacking clear regulatory information.
Validate Transactions: Always verify Bitcoin transactions using the official Bitcoin blockchain explorer by entering the recipient's address and transaction ID. Real confirmations are publicly visible, timestamped, and permanently recorded on the blockchain. A legitimate Bitcoin transaction will show the sender address, recipient address, amount transferred, transaction fee, number of confirmations, and block height. Wait for at least 3-6 confirmations before considering high-value transactions as final, as this makes reversal through blockchain reorganization virtually impossible. Never rely solely on screenshots, email confirmations, or platform notifications—always verify independently on the blockchain.
Secure Your Wallet: Use established web3 wallets that employ top-level security protocols, undergo regular independent audits, and have proven track records in the industry. Secure wallet solutions implement features like hierarchical deterministic (HD) wallet structures, hardware wallet integration, multi-signature support, and encrypted private key storage. Never store large amounts of cryptocurrency on exchange platforms—transfer funds to personal wallets where you control the private keys. Implement additional security measures including biometric authentication, strong unique passwords, and regular security updates.
Double-Check Offers: Exercise extreme caution with any offers that seem too good to be true, including steep discounts, guaranteed returns, exclusive opportunities, or urgent requests demanding immediate payment in Bitcoin. Legitimate cryptocurrency investments carry risks and never guarantee returns. Scammers create artificial urgency to prevent careful research and consideration. Take time to research any investment opportunity, verify claims through multiple independent sources, and consult with knowledgeable individuals before committing funds. Remember that legitimate opportunities will still be available after thorough research—scams disappear when scrutinized.
Educate Yourself Continuously: The cryptocurrency security landscape evolves rapidly, with new scam tactics emerging regularly. Follow updates from trusted analytical platforms and security researchers to stay informed about ongoing scam activity and best practices. Join legitimate cryptocurrency communities, attend educational webinars, and read security advisories from reputable sources. Understanding how Bitcoin and blockchain technology work fundamentally makes it much easier to identify fraudulent schemes and protect your assets effectively.
Quick Tips to Avoid Fake Bitcoin
- Only purchase from licensed, regulated exchanges with proven security records and transparent operations
- Reject all transaction requests or sales before receiving full blockchain confirmation with adequate confirmations
- Never trust "physical" Bitcoins or tokens as genuine cryptocurrency; always verify ownership on-chain through blockchain explorers
- Keep all devices, operating systems, and wallet applications updated to the latest versions with current security patches
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) using authenticator apps rather than SMS when possible
- Store recovery phrases and private keys offline in secure, physically protected locations
- Never share private keys, seed phrases, or passwords with anyone, regardless of claimed authority
- Verify website URLs carefully, checking for SSL certificates and exact domain spelling
- Research any platform or opportunity through multiple independent sources before investing
- Start with small test transactions when using new platforms or services
- Be skeptical of unsolicited investment opportunities or communications requesting cryptocurrency
Latest Trends and Unique Insights
The fake Bitcoin landscape continues to evolve with technological advancement, presenting both new challenges and improved security measures. Scammers continually adapt their tactics to exploit emerging technologies and user behaviors. According to recent analyses from leading blockchain analytics platforms, newer scam operations increasingly involve artificial intelligence and deepfake technology to mimic exchange staff, create convincing fake video testimonials, or automate sophisticated phishing campaigns at scale.
Deepfake technology has enabled scammers to create realistic video content featuring celebrities or cryptocurrency influencers promoting fraudulent schemes. These videos can be nearly indistinguishable from genuine content to untrained viewers, making verification through official channels absolutely critical. AI-powered chatbots now impersonate customer support representatives with remarkable accuracy, engaging users in convincing conversations while harvesting sensitive information or directing them toward fraudulent platforms.
Recent Bitcoin network updates have enhanced security and transaction transparency through improvements in the underlying protocol and widespread adoption of segregated witness (SegWit) and taproot upgrades. These technical improvements make certain types of attacks more difficult and provide better tools for transaction verification. However, user awareness and vigilance remain the most critical factors in preventing fraud, as most scams exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities in the Bitcoin protocol itself.
Reputable cryptocurrency exchanges have responded to evolving threats by rolling out multi-layer security checks, implementing advanced cold storage solutions for user funds, and offering insurance policies to protect against certain types of losses. Many platforms now employ artificial intelligence for fraud detection, monitoring transaction patterns for suspicious activity, implementing mandatory withdrawal delays for new accounts, and requiring additional verification for large transactions. These measures significantly reduce risk for users who choose regulated, established platforms over unverified alternatives.
Security experts and blockchain analysts consistently recommend relying exclusively on public blockchain records for transaction verification and treating any non-blockchain-based claim with immediate skepticism. The transparency of blockchain technology is one of Bitcoin's greatest strengths for security—every legitimate transaction is permanently recorded and publicly verifiable. This transparency makes it impossible for scammers to fake genuine Bitcoin transactions, though they can still deceive users through social engineering, fake platforms, and counterfeit assets that exist outside the Bitcoin blockchain.
Emerging trends in cryptocurrency security include increased regulatory oversight in major markets, development of decentralized identity solutions to prevent impersonation, improved user education initiatives by major platforms, and industry-wide collaboration to identify and shut down fraudulent operations. However, the global and decentralized nature of cryptocurrency means that user vigilance and education remain the primary defense against fake Bitcoin scams.
Takeaways on Identifying Fake Bitcoin
Understanding what a fake bitcoin looks like is a vital first step toward protecting your digital assets and building confidence in cryptocurrency markets. The key to avoiding fake Bitcoin scams lies in combining technical verification with careful platform selection and maintaining healthy skepticism toward offers that seem too advantageous.
Whether it's avoiding unverified exchanges, ignoring physical coins marketed as genuine cryptocurrency, or meticulously checking blockchain transactions through public explorers, these fundamental habits can make a tremendous difference in protecting your investments. The decentralized nature of Bitcoin provides unprecedented financial freedom, but this freedom comes with personal responsibility for security that traditional banking systems handle differently.
Use only regulated platforms with proven security records and transparent operations for trading activities. Store your digital assets in secure wallet solutions that you control, implementing strong authentication and keeping private keys absolutely confidential. With the right precautions, continuous education, and healthy skepticism, you can navigate the cryptocurrency world with confidence and avoid costly mistakes that have affected millions of users globally.
Remember that legitimate Bitcoin transactions are always verifiable on the public blockchain, genuine platforms never guarantee returns or pressure immediate action, and real cryptocurrency has no physical form. By internalizing these principles and remaining vigilant against evolving scam tactics, you can safely participate in the cryptocurrency ecosystem while protecting yourself from the various forms of fake Bitcoin that continue to plague the industry.
FAQ
How can I identify a fake Bitcoin or counterfeit cryptocurrency?
Verify transaction hashes on the public blockchain to confirm authenticity. Avoid suspicious confirmations or edited details. Check wallet addresses against official sources to prevent scams.
What are the common characteristics and red flags of fraudulent Bitcoin schemes?
Common red flags include promises of guaranteed high returns, anonymous operators, unregistered entities, pressure for quick decisions, requests for personal data, and lack of transparent operations. Avoid schemes offering unrealistic profits or requiring upfront payments.
What is the difference between a real Bitcoin and a fake or scam Bitcoin?
Real Bitcoin exists on the blockchain and can be verified cryptographically. Fake or scam Bitcoin lacks blockchain verification and is a fraudulent imitation designed to steal funds or deceive users. Always verify transactions on the blockchain.
How do Bitcoin scams work and what types of fake Bitcoin products exist?
Bitcoin scams typically involve fraudsters promoting fake cryptocurrencies or fraudulent investment schemes through social media and phishing. Common fake products include counterfeit wallets, bogus ICOs, and fraudulent trading platforms. Always verify legitimacy before investing.
What should I do if I accidentally purchase or receive a fake Bitcoin?
Report it to your wallet provider and local authorities immediately. Document all transaction details and evidence. Do not attempt to transfer or trade the fake Bitcoin, as this may complicate recovery efforts.
Are there fake Bitcoin wallets or exchanges I should avoid?
Avoid wallets and exchanges with misspelled URLs or domains impersonating legitimate platforms. Beware of requests for personal information via email. Always verify official websites before accessing them. Use reputable, established platforms with strong security records and transparent operations.

Understanding Bitcoin Wallet Addresses: A Beginner's Guide

Understanding Bitcoin Wallet Addresses: Essentials for Crypto Transactions

Top Choices for Secure Cryptocurrency Storage Devices

Ultimate Security for Your Bitcoin: Choosing the Right Hardware Wallet

Offline Cryptocurrency Storage: Enhance Security with Paper Wallets

Earn Free Cryptocurrencies with Faucet Opportunities

How Much Is 2 Pounds of Gold Worth: Latest Value & Crypto Insights
What Does Candling Mean in a Crypto Relationship?

How to Withdraw from Cryptocurrency Exchanges Efficiently

How to Delete Trust Wallet Account Safely
Can I Use Trust Wallet in New York?
