
What Happened to Twitter Stock: Key Changes Explained
Twitter Stock: From Public Listing to Private Ownership
Twitter, once a prominent fixture on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol TWTR, underwent a dramatic transformation in late 2022 that fundamentally altered its relationship with public investors. The company, which had been publicly traded since its initial public offering in November 2013, was acquired by entrepreneur Elon Musk in a landmark deal valued at approximately $44 billion. This acquisition led to Twitter's delisting from public exchanges, with the stock ceasing to trade as of October 28, 2022, effectively transitioning the company from public to private ownership.
For shareholders who had invested in Twitter stock over the years, the acquisition resulted in a mandatory buyout at $54.20 per share, as stipulated in the terms of the deal. This buyout price represented a substantial premium over the stock's trading price in the months leading up to the acquisition announcement, providing existing investors with an exit opportunity that many considered favorable given the company's fluctuating performance. However, this transition also meant that Twitter's financial performance, strategic decisions, and operational metrics would no longer be subject to the rigorous public scrutiny and regulatory disclosure requirements mandated by the Securities and Exchange Commission for publicly traded companies.
The shift to private ownership gave the new management team greater flexibility to implement strategic changes without the pressure of quarterly earnings reports and shareholder activism that often characterize public companies. This move allowed for more aggressive experimentation with the platform's features, business model, and organizational structure, though it also meant reduced transparency for users, employees, and the broader market regarding the company's financial health and direction.
Market Impact and Investor Concerns
The question of what happened to Twitter stock extends far beyond the technical mechanics of the buyout and delisting process. The removal of Twitter from public markets had significant ripple effects across the technology sector and the broader stock market ecosystem. Institutional investors and portfolio managers who had previously used Twitter as a key benchmark for social media and digital advertising performance were forced to adjust their investment strategies and seek alternative indicators to gauge the health of the social media industry.
The delisting also highlighted a growing trend of high-profile technology companies transitioning from public to private ownership, often driven by founders or major investors seeking to pursue long-term strategic changes away from the short-term pressures and volatility associated with quarterly reporting and public market expectations. This trend has raised questions about the future of public markets for technology companies and whether the traditional IPO path remains the most attractive option for scaling businesses.
Another critical concern that emerged from Twitter's privatization was the fate of employee compensation tied to equity. Thousands of Twitter employees held stock options and restricted stock units (RSUs) that were suddenly affected by the change in ownership structure. In most cases, these equity instruments were converted to cash payments based on the $54.20 per share acquisition price, or in some instances, rolled into new private equity arrangements depending on the specific terms negotiated during the acquisition process. This conversion process underscored the complexities and potential disruptions involved when a major public company transitions to private ownership, affecting not only large institutional investors but also the financial planning and wealth accumulation of thousands of individual employees who had relied on equity compensation as a significant portion of their total compensation package.
Furthermore, the delisting removed a liquid trading venue for investors who might have wanted to adjust their positions based on the company's evolving performance under new management, creating a situation where former shareholders had limited options for re-entering or exiting their positions in the company's future.
Broader Trends: Digital Assets and Financial Innovation
While what happened to Twitter stock represents a unique case study in corporate restructuring and market dynamics, it also reflects broader shifts in how technology companies interact with financial markets and how investors access exposure to innovative sectors. The traditional model of public equity markets is being challenged and complemented by the rapid rise of digital assets, including cryptocurrencies, tokenized securities, and blockchain-based financial instruments that offer new pathways for capital formation and investment.
For example, the financial landscape has witnessed significant innovation in how investors gain exposure to emerging technologies. As of October 29, 2025, Grayscale Investments launched a Solana-focused exchange-traded fund (GSOL) on NYSE Arca, providing investors with regulated exposure to blockchain assets that include staking rewards.
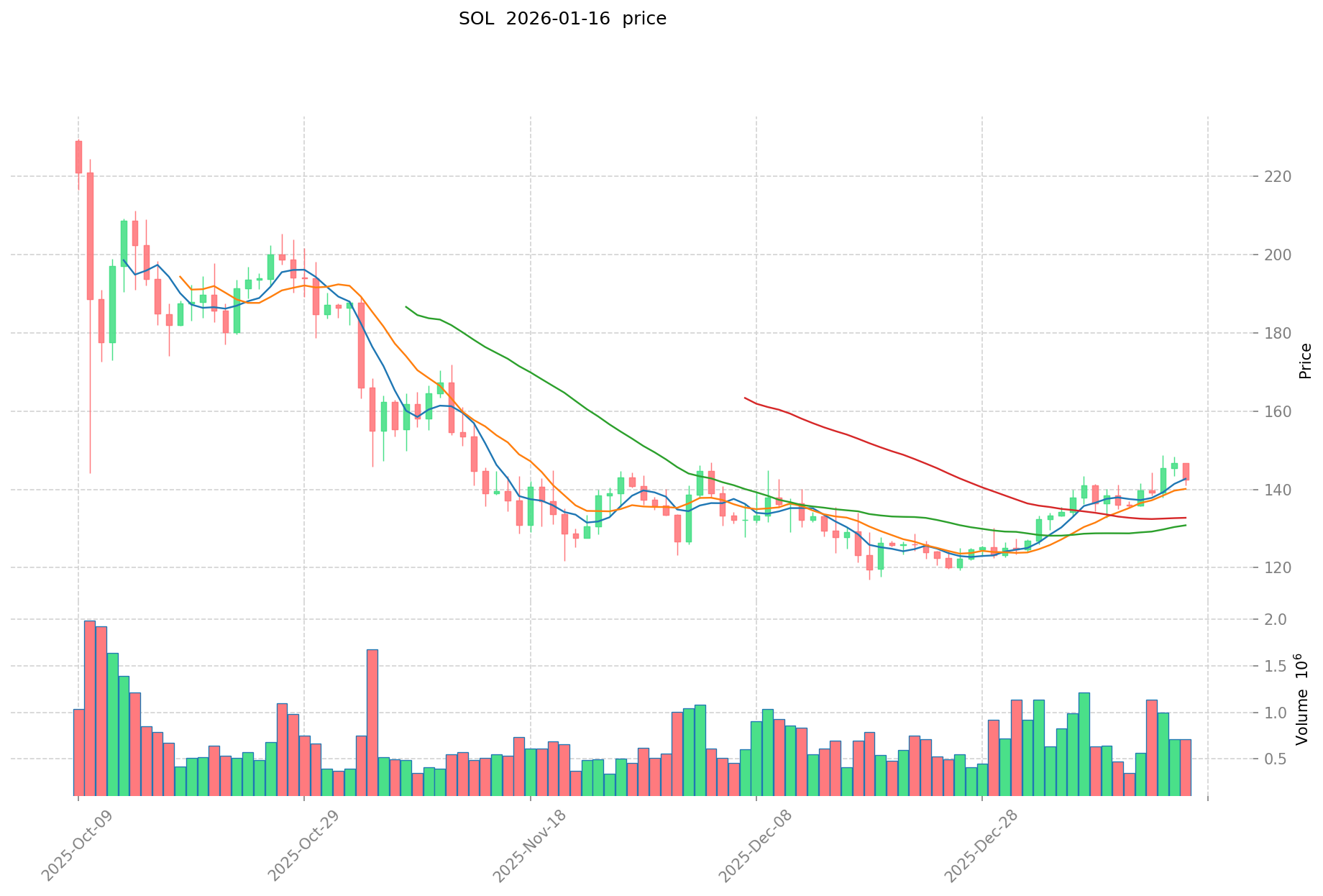 This development demonstrates the increasing integration of traditional finance infrastructure with digital asset markets, creating hybrid investment products that bridge the gap between conventional securities and cryptocurrency ecosystems.
This development demonstrates the increasing integration of traditional finance infrastructure with digital asset markets, creating hybrid investment products that bridge the gap between conventional securities and cryptocurrency ecosystems.
Such innovations provide investors with new opportunities for portfolio diversification and potential yield generation through mechanisms like staking, which allows token holders to earn rewards by participating in blockchain network validation. However, these new investment vehicles also introduce novel risks and regulatory considerations that investors must carefully evaluate, including custody risks, technological vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty, and the volatility inherent in emerging asset classes.
The transition of Twitter from a publicly traded stock to a private entity can be viewed as part of this larger narrative where companies and investors are exploring more flexible capital structures and alternative funding mechanisms. Some private companies are leveraging blockchain technology to create tokenized equity or using alternative trading platforms to provide liquidity to shareholders outside of traditional public exchanges. These developments suggest that the future of corporate finance and investment may involve a more diverse ecosystem of funding and trading mechanisms beyond the conventional public stock market model.
Additionally, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and tokenized assets is creating new ways for companies to raise capital and for investors to participate in growth opportunities, potentially reducing reliance on traditional IPO processes and public market listings. This evolution in financial infrastructure may reshape how companies like Twitter might approach capital raising and shareholder liquidity in the future.
Key Takeaways and Next Steps
For investors and market observers seeking to understand what happened to Twitter stock, the answer centers on its acquisition by Elon Musk, subsequent delisting from public exchanges, and transformation into a privately held company. This event serves as an important case study illustrating how market dynamics, corporate strategy, regulatory environments, and individual leadership decisions can converge to fundamentally reshape the investment landscape and alter the relationship between companies and their stakeholders.
The Twitter delisting highlights several important lessons for investors: the importance of understanding the risks associated with concentrated positions in individual stocks, the potential for sudden corporate actions that can remove liquidity, and the evolving nature of technology company ownership structures. It also underscores the value of diversification across different asset classes and investment vehicles to mitigate the impact of such transformative events.
As digital assets, blockchain technology, and innovative financial products continue to emerge and mature, staying informed about these developments becomes increasingly critical for investors seeking to navigate the complex and rapidly evolving financial landscape. The integration of traditional finance with digital asset markets is likely to accelerate, creating both opportunities and challenges that require careful analysis and risk management.
For those who were former Twitter shareholders or employees affected by the privatization, understanding the tax implications of the buyout and exploring alternative investment opportunities in the social media and technology sectors may be important next steps. Additionally, keeping abreast of how the company evolves under private ownership and whether any future liquidity events might occur could provide insights into the long-term outcomes of this significant corporate transformation.
Ultimately, the story of what happened to Twitter stock is not just about one company's journey from public to private ownership, but rather a reflection of broader trends in corporate governance, financial innovation, and the changing relationship between technology companies and capital markets in an increasingly digital economy.
FAQ
When did Elon Musk acquire Twitter, and what was the transaction price?
Elon Musk announced the acquisition of Twitter on April 14, 2022, at USD 54.20 per share, with a total transaction amount of USD 44 billion. The deal was subsequently terminated in July 2022.
What happened to Twitter stock during its transition from public to private?
Twitter stock was delisted from public exchanges after going private in 2021. Share prices became illiquid and less volatile. Former shareholders could no longer trade publicly, marking the end of its tenure as a public company.
What impact did Musk's acquisition of Twitter have on existing shareholders and investors?
Musk's acquisition led to significant changes for Twitter shareholders. Original stockholders received cash payment at $54.20 per share, providing liquidity. The acquisition removed Twitter from public markets, fundamentally transforming its ownership structure and business strategy under new management.
What happens to investor shares after Twitter's privatization?
After Twitter's privatization, investor shares are converted to cash at the acquisition price. Shareholders receive buyout compensation and exit the public market. The stock no longer trades publicly.
Why did Elon Musk acquire Twitter, and what were his main objectives?
Elon Musk acquired Twitter to defend free speech and unlock the platform's commercial potential. His primary goals were to improve user experience, transform Twitter into a more open digital town square, and explore new business opportunities including monetization features and technological innovation.
What are the major business and operational changes at Twitter before and after the acquisition?
Post-acquisition, Twitter underwent significant restructuring including management reorganization, workforce reduction, and introduction of new revenue models combining advertising with paid premium features.
Twitter stock delisting from NASDAQ: specific timing and reasons?
Twitter delisted from NASDAQ on October 27, 2022, following Elon Musk's $44 billion acquisition. The company transitioned to private ownership, ending public trading and concluding its tenure as a publicly listed entity on the exchange.
What are the key timeline milestones and significant events in the Twitter acquisition deal?
Key milestones include April 2022 when Elon Musk proposed acquiring Twitter for 44 billion USD. The acquisition officially completed in October 2022. In April 2023, Musk announced plans to redesign Twitter's platform and features.
Exploring How Cross-Chain Bridges Operate in Blockchain Systems

How Did Telegram's Security Risks Evolve in 2025?

What are the key fundamentals to analyze in a crypto project's whitepaper?

How Does TON's Community and Ecosystem Activity Compare to Other Cryptocurrencies in 2025?

How to Analyze NEAR Protocol's On-Chain Data: Key Metrics and Growth Trends

How Will Chainlink's Fundamentals Impact LINK's Price in 2030?

What Does On-Chain Data Analysis Reveal About Active Addresses, Whale Movements, and Transaction Volumes?
How does Federal Reserve policy and inflation data impact CAKE token price in 2026?

How do exchange inflows and outflows affect crypto holdings and market flow in 2026?

How do Fed policy, inflation data, and stock market volatility affect crypto prices in 2026?
How to Send BTC on Cash App
