What is token economics model and how do allocation, inflation, and burn mechanisms work
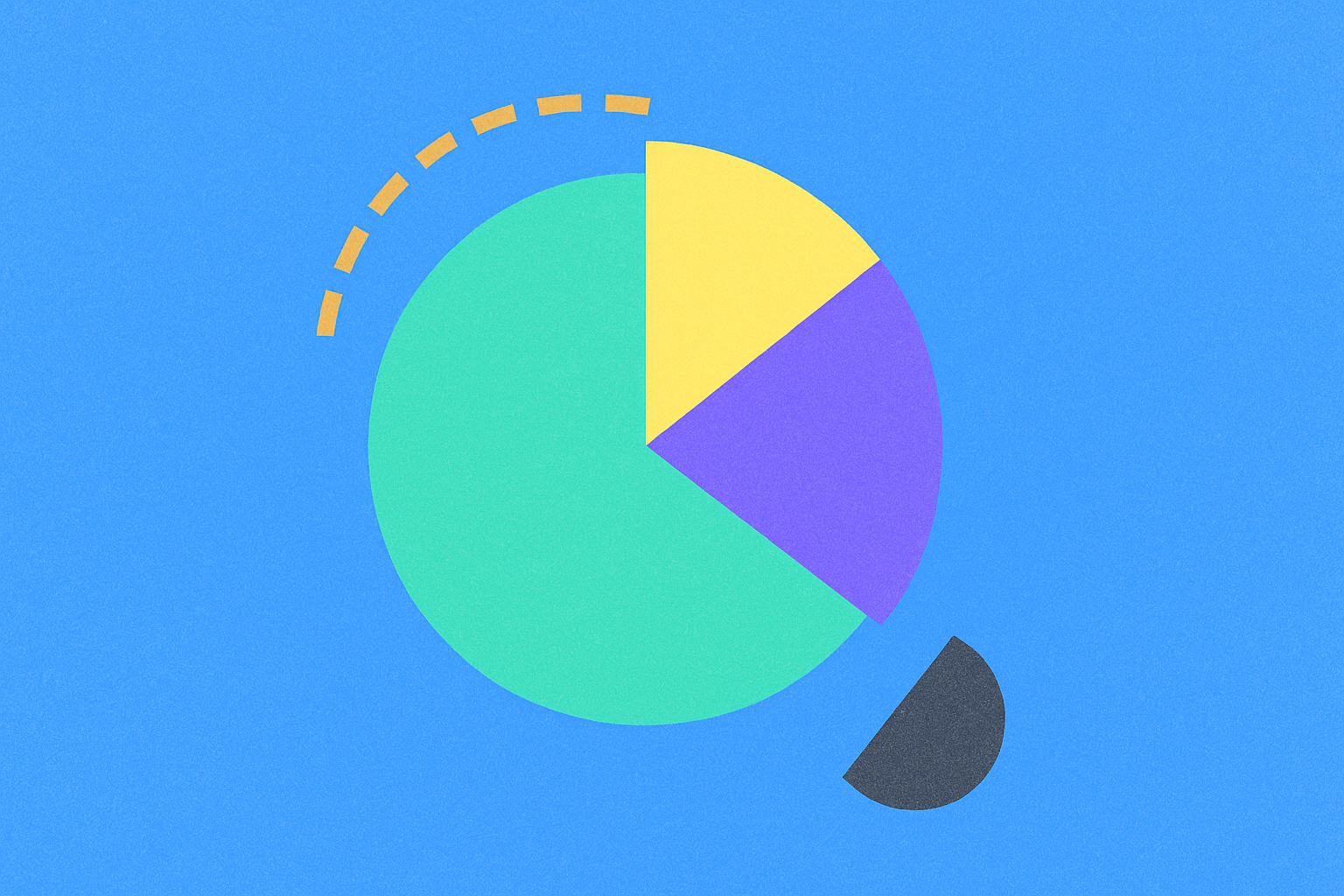


Token allocation fundamentals: typical distribution ratios across team (20-30%), investors (20-30%), and community (40-60%) segments
Effective token allocation establishes the foundation for a project's long-term viability and community trust. The distribution ratios across major stakeholder segments follow established patterns that balance innovation incentives with broader accessibility. Team allocations typically represent 20–30% of total supply, rewarding developers, advisors, and core contributors for building and maintaining the project. This range ensures sufficient motivation for key personnel without creating excessive centralization in early hands.
Investor allocations, also commonly 20–30%, reflect capital requirements and risk compensation for those funding project development. These stakeholders provide crucial resources during bootstrap phases. Meanwhile, community allocations constitute 40–60% of total supply, deliberately positioned as the largest segment. This ratio emphasizes inclusive participation and demonstrates the project's commitment to decentralized ownership.
The rationale underlying these distribution ratios directly influences token economics behavior. When community segments represent the majority, projects create broader holder bases that enhance network effects and adoption potential. Conversely, balanced team and investor portions prevent excessive selling pressure while maintaining sufficient resources for operations. Real-world projects demonstrate that maintaining these proportions supports healthy price dynamics and stakeholder alignment. Deviations—whether over-allocating to teams or under-allocating to communities—frequently result in market skepticism and reduced participation. Understanding these allocation fundamentals reveals how token distribution shapes both immediate incentives and long-term ecosystem sustainability within the broader token economics model.
Inflation and deflation mechanics: designing sustainable emission schedules and token release mechanisms to maintain ecosystem value
Designing effective emission schedules represents a foundational element of sustainable tokenomics. Inflation mechanics determine how new tokens enter circulation over time, directly influencing token scarcity and long-term value preservation. A well-structured emission schedule gradually releases tokens according to predetermined parameters, preventing sudden supply shocks that could destabilize ecosystem economics. For instance, tokens with defined total supplies like the 1 billion token cap demonstrate how hard supply limits create predictable inflation curves.
Deflation mechanics operate through token burning and removal mechanisms that counter excessive supply growth. When protocols implement burning strategies—whether through transaction fees, governance actions, or algorithmic triggers—they reduce circulating supply and create deflationary pressure. This counterbalance to inflation helps maintain ecosystem stability. The interplay between these mechanisms requires careful calibration; aggressive inflation without corresponding deflation mechanisms weakens token economics, while excessive deflation may inhibit network utility and growth.
Sustainable token release mechanisms must balance community incentives, long-term viability, and price stability. Emission schedules typically incorporate vesting periods, gradual unlock phases, and conditional releases tied to ecosystem milestones. By spacing token releases strategically, projects maintain healthy circulation ratios while preventing large holders from destabilizing markets through sudden supply floods. These carefully engineered mechanics ultimately determine whether an ecosystem can sustain long-term value creation or faces inevitable economic collapse.
Burn and buyback strategies: reducing circulating supply through transaction fees, governance mechanisms, and protocol-level deflationary measures
Token burn mechanisms and buyback strategies represent critical tools for managing circulating supply and influencing token value dynamics within cryptocurrency ecosystems. These deflationary measures operate through multiple channels, each designed to systematically reduce the number of tokens available in active circulation. Transaction fee mechanisms automatically allocate a percentage of network fees to permanent removal or redemption pools, creating continuous, predictable token reduction proportional to network activity.
Governance mechanisms empower token holders to vote on burn schedules and buyback parameters, democratizing supply management decisions. Protocols often implement automated buyback programs funded by protocol revenues, repurchasing tokens from secondary markets at predetermined intervals before permanently removing them from circulation. This approach creates buy-side market pressure while achieving deflationary objectives. Protocol-level deflationary measures operate at the infrastructure level, embedding burn logic directly into consensus mechanisms or reward distribution systems. Real-world implementations demonstrate these strategies' effectiveness—tokens allocating significant portions to deflationary mechanisms often maintain healthier supply ratios. Platforms utilizing multi-layered burn approaches typically experience more stable tokenomics than those relying on single mechanisms, as diversified deflationary strategies provide resilience against market volatility and ensure consistent circulation reduction regardless of network conditions or governance participation rates.
Governance tokenomics: aligning holder incentives with protocol decisions through voting rights and reward distributions
Governance tokenomics represents a critical framework where protocol communities align individual holder incentives with collective decision-making through voting rights and reward mechanisms. Token holders receive proportional voting power based on their holdings, enabling them to participate directly in protocol governance decisions. This structure transforms passive token ownership into active participation, creating financial incentives for holders to make decisions that enhance long-term protocol value. Reward distributions form the economic backbone of this alignment, compensating voters for their involvement and decision-making contributions. Governance tokens typically grant weighted voting privileges, where larger holders possess greater influence proportional to their stake, similar to how distributed token supplies across hundreds of thousands of addresses create diverse stakeholder perspectives. The allocation of governance tokens itself reflects protocol philosophy—whether through initial community distributions, staking rewards, or contributor compensations. These mechanisms ensure holders remain economically invested in protocol outcomes. When token rewards accrue from governance participation and successful protocol decisions, holders develop stronger commitment to the ecosystem. Effective governance tokenomics balances voting power concentration risks with meaningful incentive structures, ensuring active participation while preventing dominance. The interaction between allocation mechanisms, voting frameworks, and reward distributions creates self-reinforcing cycles where engaged token communities drive better protocol decisions, ultimately strengthening tokenomics sustainability and protocol resilience.
FAQ
What is a token economics model and why is it important for crypto projects?
Token economics defines supply, distribution, and incentive mechanisms. It's crucial because it determines token value sustainability, controls inflation through burn/allocation, aligns stakeholder interests, and ensures long-term project viability by balancing supply dynamics with demand.
What types of token distribution mechanisms exist? What are reasonable proportions for initial allocation, team allocation, and community allocation?
Common distribution types include: Initial allocation (40-50%), Team allocation (15-20%), Community/Airdrop (20-30%), Reserve/Treasury (10-15%), and Advisor allocation (5-10%). Optimal ratios depend on project stage and goals, but balanced allocations with strong community incentives typically perform better long-term.
What does token inflation mean? How do high and low inflation affect token price?
Token inflation refers to the increase in circulating supply over time through new token issuance. High inflation typically increases supply, potentially pressuring prices downward unless demand grows proportionally. Low inflation reduces supply growth, generally supporting price appreciation by creating scarcity and limiting dilution of existing token holders.
How does the token burn mechanism work? What are the benefits of burning tokens for the project ecosystem?
Token burning removes tokens from circulation permanently, reducing total supply. This increases scarcity and potential value per token. Benefits include: reducing inflation, improving tokenomics, incentivizing holding, and enhancing long-term sustainability. Burns strengthen ecosystem confidence and stability.
How do allocation, inflation, and burn mechanisms work together?
Allocation distributes tokens to stakeholders at launch. Inflation increases supply over time to incentivize participation. Burn removes tokens from circulation to reduce supply. Together, they balance token availability, maintain value stability, and align incentives across the ecosystem.
How to assess the health of a token economics model?
Evaluate token health by analyzing: allocation fairness across stakeholders, inflation rate sustainability, burn mechanisms effectiveness, trading volume trends, holder distribution, and long-term supply dynamics. Healthy models show balanced incentives, controlled dilution, and active utility adoption.

Cryptography Fundamentals Explained: Understanding the Basics

Understanding the Basics of Cryptography in Computer Networks

Understanding Merkle Roots in Blockchain Technology

Understanding the Fundamentals of Cryptography

Understanding Merkle Trees in Cryptography Basics

Understanding Cryptographic Hash Algorithms in Modern Security

Unveiling zkLink: A New Age in Multi-Chain Infrastructure

What is the difference between competing cryptocurrency projects in market cap and performance?

What is a token economy model: allocation mechanisms, inflation design, and governance utility explained

Beware of Offline USDT Transaction Scams
What is cryptocurrency holding and capital flow: exchange inflows, staking rates, and on-chain concentration explained
