Exploring The Benefits of DAG Technology in Blockchain Systems

What is a directed acyclic graph (DAG)?
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is an innovative technology in the cryptocurrency space that has gained attention as a potential alternative to traditional distributed ledger systems. This article explores the concept of DAG, its workings, and how it compares to other technologies.
DAG vs traditional distributed ledger technology
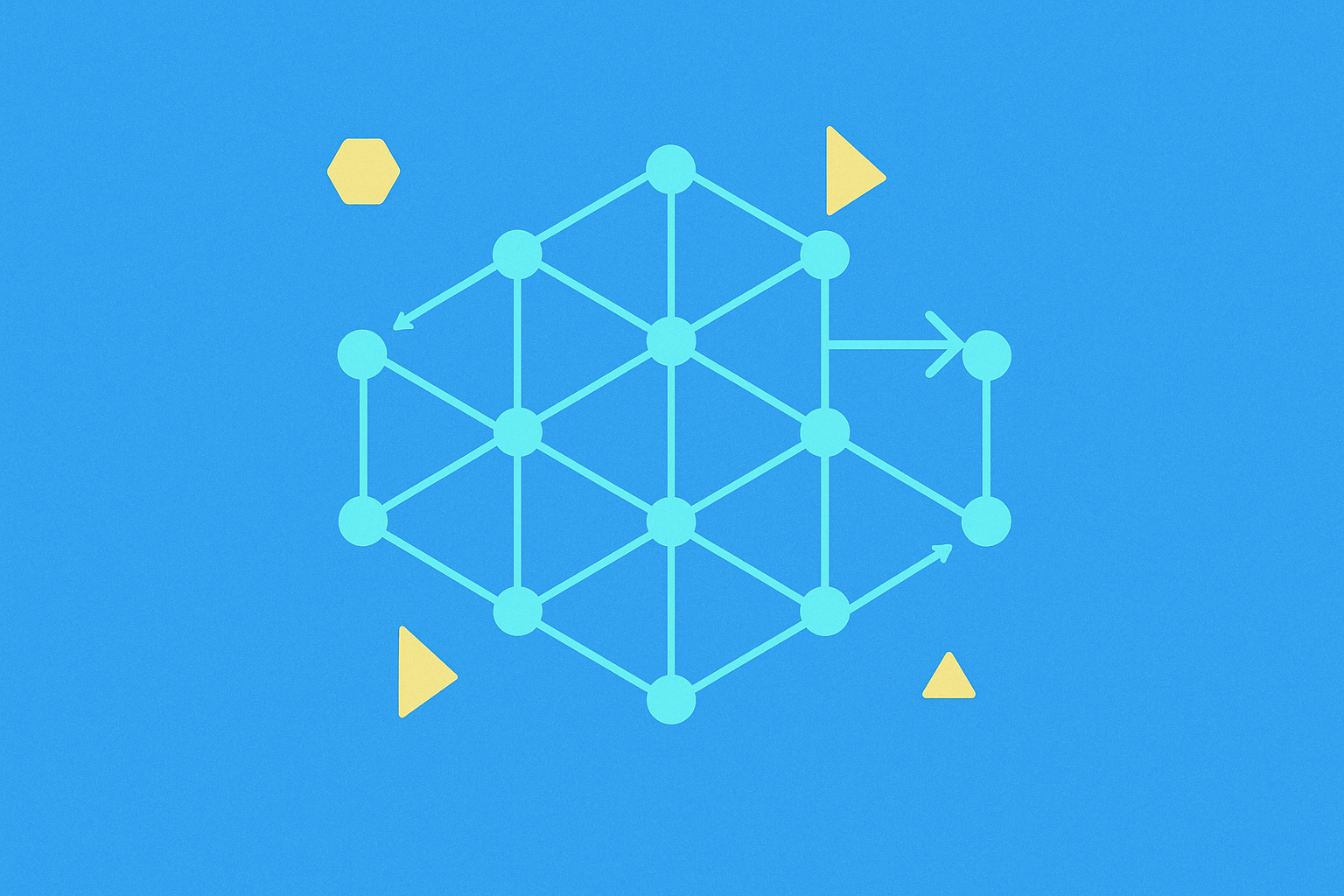
DAG is a data modeling tool used by some cryptocurrencies instead of a conventional distributed ledger. It's sometimes referred to as a potential "game-changer" due to its advantages. The DAG architecture uses circles (vertices) to represent activities and lines (edges) to show the order of transaction approvals. Unlike traditional systems, DAG doesn't gather transactions into blocks but builds them on top of each other, significantly improving transaction speed.
What's the difference between a DAG and a conventional distributed ledger?
While both DAGs and conventional distributed ledgers serve similar roles in the crypto industry, they have distinct differences. DAGs don't create blocks like traditional systems do. Instead, they build transactions on top of previous ones. Visually, conventional systems look like a chain of blocks, while DAGs resemble graphs with circles and lines.
How does DAG technology work?
In a DAG-based system, each circle (vertex) represents a transaction. To make a transaction, a user must first confirm a previous unconfirmed transaction (called a "tip"). Once confirmed, their transaction becomes the new tip, waiting for the next user to confirm it. This process creates layers of transactions, allowing the system to grow continuously. DAG also includes a mechanism to prevent double-spending by assessing the entire transaction path back to the first transaction.
What is DAG used for?
DAG technology is primarily used for processing transactions more efficiently than traditional systems. It offers several advantages:
- Faster transaction processing due to the absence of blocks
- Energy efficiency, as it doesn't rely on traditional mining
- Suitability for micropayments due to low or no transaction fees
- Ability to handle high transaction volumes without congestion
Which cryptocurrencies use DAG?
Several cryptocurrency projects have adopted DAG technology:
- IOTA (MIOTA): Known for fast transactions, scalability, and data integrity
- Nano: Combines DAG and distributed ledger technology for quick, fee-less transactions
- BlockDAG: Offers energy-efficient mining of BDAG tokens
DAG pros and cons
DAG technology has several advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- High transaction speed
- Zero or low fees
- Energy efficiency
- Excellent scalability
Cons:
- Potential decentralization issues
- Limited testing at scale
Conclusion
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) technology presents an intriguing alternative to conventional distributed ledger systems in the cryptocurrency space. With its advantages in transaction speed, scalability, and energy efficiency, DAG has the potential to address some of the limitations of traditional systems. However, it also faces challenges, particularly in terms of decentralization and large-scale implementation. As the technology continues to evolve, it will be interesting to see how DAG develops and whether it can overcome its current limitations to become a viable competitor to conventional systems in the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem.
FAQ
What is a directed acyclic graph?
A directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a data structure used in some cryptocurrencies. It allows for faster, more scalable transactions than traditional blockchain by organizing data in a network of nodes without circular dependencies.
What is DAG used for?
DAG is used for faster, scalable transactions in cryptocurrencies, enabling parallel processing and improved efficiency compared to traditional blockchain systems.
What is DAG with example?
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a data structure used in some cryptocurrencies. Example: IOTA uses Tangle, a DAG-based system, for faster and fee-less transactions.
Is DAG better than blockchain?
DAG and blockchain have different strengths. DAG offers faster transactions and better scalability, while blockchain provides higher security and decentralization. The 'better' choice depends on specific use cases and requirements.

Exploring the Polkadot Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Guide to Blockchain Innovation

How to Measure Crypto Community Engagement: Key Metrics Revealed

Exploring Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology

Exploring Directed Acyclic Graph Technology in Blockchain Systems

Exploring DAG Technology in Blockchain: A New Frontier

Bitcoin vs. Ethereum: Which Crypto is the Better Long-Term Investment?

Aptos Mainnet Launch and Noteworthy Ecosystem Projects
Decentralized Perpetual Exchange GMX Integrates Leading Multi-Chain Wallet for Enhanced Trading Access

How can I access my wallet’s private key or mnemonic phrase?

What is TON PUNKS?