The Complete Guide to Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): Understanding Its Operating Principles and Ecosystem in 3 Minutes

What Are Smart Contracts? Introduction to 3 Key Operating Elements
Smart contracts are computer programs or applications that operate autonomously on blockchain networks. They consist of data code deployed by developers to execute specific instructions. Users cannot control smart contracts because they run automatically according to their programming design. Smart contracts represent a revolutionary advancement in blockchain technology, enabling automated execution of agreements without intermediaries.
The Ethereum network was the first blockchain to implement smart contracts successfully. As a result, millions of smart contracts have been coded and deployed on the Ethereum blockchain over the years. The EVM has played a crucial role in achieving this remarkable feat, serving as the computational engine that powers the entire ecosystem.
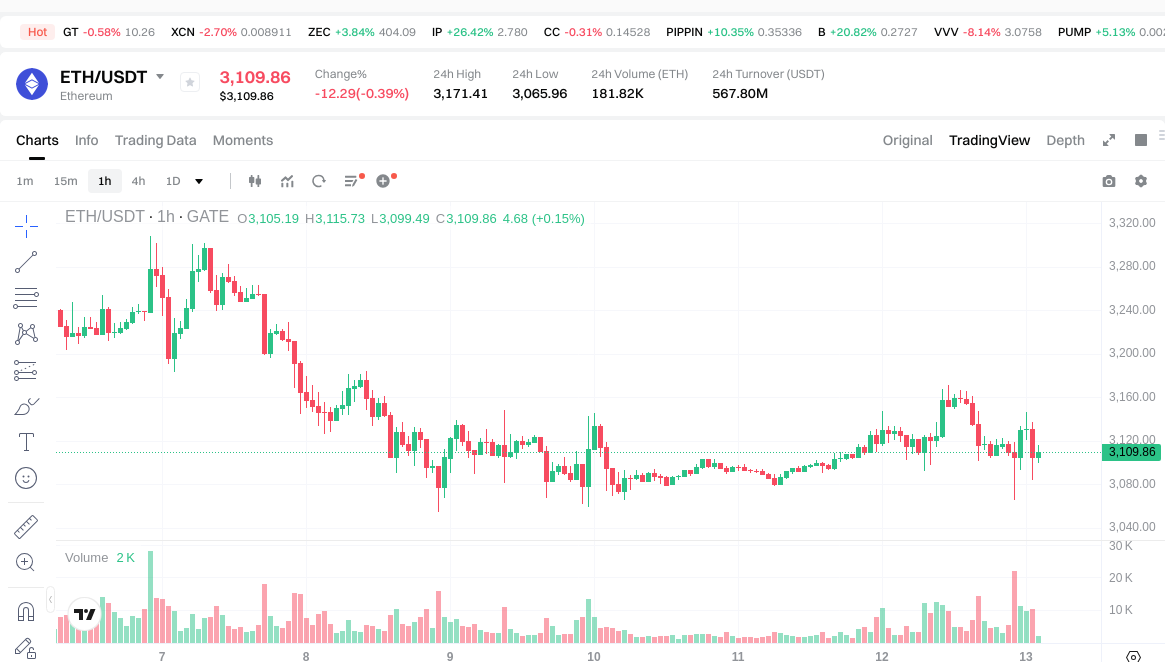
Smart Contract Element 1: Programming Language
The most widely used computer language for creating Ethereum smart contracts is Solidity. Like JavaScript, it is a high-level language suitable for human understanding, but machines cannot directly interpret it. Therefore, once developers write smart contracts in Solidity, they must translate them into machine language or bytecode using an Ethereum Virtual Machine compiler such as solc. This compilation process is essential for converting human-readable code into executable instructions that the EVM can process. The compilation step ensures that the code is optimized for efficient execution while maintaining security standards.
Smart Contract Element 2: Smart Contract Execution
When the EVM executes code, the Gas supply decreases according to the Gas cost of performing computations. If at any time before the transaction completes, the Gas supply reduces to zero, the EVM immediately stops execution. It abandons the transaction and makes no changes to the world state, protecting the network from incomplete or malicious operations. The network remains unaffected, but the sender's ETH balance decreases to pay for the computational costs used to execute the code up to the stopping point. However, if execution completes successfully, the EVM updates the world state to match the machine state version, ensuring data consistency across the network.
Smart Contract Element 3: Ethereum Gas Fees
From the above explanation, we can see that Gas fees play a crucial role in transaction processing on the Ethereum blockchain. When Ethereum used the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, processing transactions required hardware and electricity, and miners needed incentives to perform their tasks. In the case of processing ETH token transfers, Gas fees vary according to network congestion levels.
During smart contract execution, Gas fees serve a different role. When executing, smart contract bytecode is broken down into smaller parts called "opcodes." Opcodes, short for operation codes, are instructions that the EVM uses to perform computations. Each opcode is assigned a certain Gas fee—the more complex the opcode, the higher the cost. This step is critical for protecting the Ethereum blockchain from malicious attacks. For example, if a user deploys a DDoS attack, the EVM will continue to execute the smart contract in the machine state. It charges Gas fees for each computation, and when the sender runs out of Gas, it will abandon the transaction, effectively preventing resource exhaustion attacks.
What Is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)? Analysis of 2 Operating States
The EVM is built into the core of the Ethereum protocol. As its name suggests, the EVM is a virtual machine or digital software that supports the operation of the Ethereum network. Virtual machine software can execute programs, store data, connect to networks, and perform other computational tasks. It is also responsible for the code execution and deployment of smart contracts, serving as the computational backbone of the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
Because Ethereum processes more than just peer-to-peer value transactions, it requires a more sophisticated computing system. Therefore, instead of calling the network a distributed ledger, Ethereum developers refer to it as a "state machine with unlimited states." This describes the fundamental concept of how the EVM works. The Ethereum network contains two types of states: the world state and the machine state, each serving distinct but complementary purposes.
EVM Operating State 1: World State
The world state is where Ethereum stores its account balances and smart contracts. Similar to the Bitcoin ledger, it is decentralized, immutable, and accessible to everyone online. The EVM updates this layer every time it completes a transaction, ensuring that all participants have access to the same information. This means that anyone with a block explorer can view the Ethereum blockchain and see the same data in real-time. The world state represents the current snapshot of all accounts, balances, and contract storage, providing a transparent and verifiable record of the network's status.
EVM Operating State 2: Machine State
The machine state is where the EVM processes transactions step by step. It is also commonly referred to as the Ethereum sandbox for developers, providing an isolated environment for code execution. The Ethereum network processes two types of transactions. The first type is "message calls"—when one account transfers ETH tokens to another account. In this case, the EVM transfers ETH tokens from one wallet address to another, then updates the transaction on the world state. The sender needs to pay Gas fees for the computations completed when sending the transaction. The machine state allows for temporary modifications and calculations before committing final changes to the world state, ensuring transaction atomicity and consistency.
Advantages and Limitations of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): What Are the Benefits and Constraints?
Advantages of EVM
As mentioned above, the EVM prevents malicious activities from attacking the network through its Gas fee mechanism and execution controls. Therefore, it can execute smart contracts and other automated services on a secure and reliable platform. The Ethereum network has the largest crypto ecosystem, serving as the gold standard for DApp creation and smart contract deployment.
Many other blockchains have created sidechains that allow Ethereum developers to transfer their applications without changing code, demonstrating the EVM's widespread adoption and compatibility. This interoperability has fostered innovation and reduced development costs across the blockchain industry.
At the same time, the EVM is decentralized, meaning anyone can create smart contracts on Ethereum without permission. It also enables developers to build and deploy decentralized services and applications that have gained widespread popularity in recent years. This permissionless nature has democratized access to blockchain technology, allowing developers worldwide to contribute to the ecosystem.
Limitations of EVM
The EVM has two significant limitations. First, it requires users to have prior knowledge and coding skills in Solidity. Many people need help with coding aspects, making it difficult for new users to create and interact with smart contracts. This technical barrier has limited mainstream adoption and requires educational initiatives to overcome.
Its second limitation is that when creating smart contracts or deploying applications on the Ethereum network, Gas fees can become very expensive, especially during periods of high network congestion. These high costs can make certain use cases economically unfeasible and have driven the development of Layer 2 solutions and alternative blockchain platforms.
EVM Ethereum Virtual Machine Ecosystem Sharing: 5 Major EVM Use Cases
As the Ethereum Virtual Machine executes smart contracts, many new innovations have entered the blockchain field. The following are the top five EVM use cases that demonstrate the versatility and power of this technology:
EVM Ecosystem Use Case 1: ERC-20 Tokens
ERC-20 tokens are generated by smart contracts using predefined data structures. The data structure is responsible for naming, distributing, and tracking tokens, providing a standardized framework for token creation. In 2017, when Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) were popular, many new cryptocurrencies were launched using ERC-20 tokens. In recent years, the best use of ERC-20 tokens has been for stablecoins such as USDT, which provide price stability and facilitate trading across decentralized platforms. The ERC-20 standard has become the foundation for tokenization in the blockchain industry.
EVM Ecosystem Use Case 2: Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Decentralized exchanges (DEX) allow users to buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies by deploying smart contracts that eliminate intermediaries. Exchanges like Uniswap and SushiSwap also use Automated Market Maker (AMM) applications, allowing users to leverage token liquidity pools without third-party intervention. These platforms have revolutionized cryptocurrency trading by providing transparent, permissionless access to financial markets while maintaining user custody of assets throughout the trading process.
EVM Ecosystem Use Case 3: NFT
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are digital artworks stored on the blockchain that verify ownership and cannot be replicated. Blockchain enthusiasts use smart contracts to create and mint NFT collections, establishing provable scarcity and authenticity. Some of the most valuable NFT collections include Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) and CryptoPunks. Owners can transfer or trade their NFTs on marketplaces such as OpenSea, creating a vibrant secondary market for digital collectibles and art.
EVM Ecosystem Use Case 4: DeFi Lending
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) lending refers to platforms that allow users to lend or borrow cryptocurrencies without using third parties. Smart contracts manage lending protocols, automating the entire process from loan origination to repayment. Loans are issued immediately to borrowers, and lenders sometimes receive interest payments on a daily basis. This innovation has democratized access to financial services, enabling users worldwide to earn yield on their crypto assets or access liquidity without traditional banking infrastructure.
EVM Ecosystem Use Case 5: Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are public entities that lack central authority, operating through collective decision-making processes. In a DAO, individual members collectively make management decisions about projects through voting mechanisms encoded in smart contracts. The rules of DAOs are established by core community members and enforced through smart contracts, ensuring transparent and democratic governance. This organizational structure represents a new paradigm for coordination and collaboration in the digital age.
Cryptocurrency and EVM Compatibility: Which Cryptocurrencies Are Compatible with EVM?
EVM-compatible blockchains provide a simple solution to the problem of expensive Gas fees while maintaining compatibility with Ethereum's developer ecosystem. Developers have borrowed certain parts of the Ethereum network and created DApps that enable users to quickly and easily move assets between any EVM networks. Among the widely adopted blockchains that follow this EVM compatibility approach, the main ones include:
- Leading Smart Chain Platforms
- Avalanche
- Fantom
- Cardano
- Polygon
- Tron
These EVM-compatible chains offer developers the flexibility to deploy their applications across multiple networks while leveraging existing Ethereum tools and infrastructure. This multi-chain approach has fostered innovation and competition, driving improvements in scalability, transaction costs, and user experience across the blockchain ecosystem.
Future Outlook for EVM Ethereum Virtual Machine: Latest Trends Driving Smart Contracts
Building on Bitcoin's foundation, Vitalik Buterin's vision was to create a decentralized supercomputer that everyone could access virtually. The Ethereum Virtual Machine has played a tremendous role in realizing this vision, transforming blockchain from a simple transaction ledger into a global computing platform. Since its conception, the EVM has undergone multiple upgrades and continues to evolve and improve, incorporating new features and optimizations.
Given that smart contract applications have driven the latest major trends in blockchain technology, including DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs, it is amazing to imagine what this technology will unlock in the future. As the ecosystem matures and new scaling solutions emerge, the EVM is poised to power the next generation of decentralized applications, potentially revolutionizing industries from finance to supply chain management, gaming, and beyond. The continued development of Layer 2 solutions, cross-chain bridges, and improved developer tools promises to make the EVM more accessible and efficient, further expanding its impact on the global digital economy.
FAQ
What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)? What is its core function?
EVM is Ethereum's sandbox execution environment for smart contracts. It compiles Solidity code into bytecode and executes it securely. Its core function is to ensure deterministic contract execution, manage gas costs, and maintain state consistency across the network.
How does EVM execute smart contracts? What are its operating principles?
EVM executes smart contracts by loading compiled bytecode and running it instruction-by-instruction using a stack-based model. It processes opcodes in isolation, maintaining a sandbox environment where contract code cannot access networks or external systems. State changes are recorded on the blockchain through gas-metered execution.
What are the differences between EVM and other blockchain virtual machines like Solana VM?
EVM uses contract-based storage management and sequential execution, while Solana VM employs an account model with parallel processing. EVM prioritizes security through state isolation, whereas Solana VM focuses on throughput optimization through account-level concurrency.
What programming languages and tools are needed to develop smart contracts on EVM?
Smart contracts on EVM primarily use Solidity programming language. Essential development tools include Hardhat and Truffle for compilation, testing, and deployment. Web3.js or Ethers.js libraries facilitate blockchain interaction.
How does the EVM Gas fee mechanism work?
EVM Gas measures computational power needed for operations. Gas consumption includes execution and message calls. Fees are calculated dynamically based on complexity, paid by users to ensure transaction processing.
What are the main Layer 2 scaling solutions in the EVM ecosystem?
The primary Layer 2 solutions include Optimism, Polygon 2.0, Mantle, and zkSync. These solutions enhance Ethereum's scalability and transaction throughput through rollup technology and zero-knowledge proofs.
How to ensure the security of smart contracts deployed on EVM?
Ensure EVM smart contract security by conducting rigorous code audits, avoiding non-deterministic operations like random numbers and timestamps, performing comprehensive testing, and utilizing formal verification tools to detect vulnerabilities before deployment.
What are EVM-compatible chains? Why do these chains choose EVM compatibility?
Major EVM-compatible chains include BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Arbitrum, and Optimism. They adopt EVM compatibility to leverage Ethereum's existing developer tools, wallets like MetaMask, and smart contracts, enabling faster ecosystem growth and seamless user migration while reducing development complexity.

Monthly Active User Statistics for a Leading Web3 Wallet

Understanding ENS: A Comprehensive Guide to Ethereum Name Service
Understanding Polygon Blockchain: A Comprehensive Guide

How Will Ethereum's Market Cap Evolve by 2030?

Understanding Polygon on the Ethereum Network

How does Ethereum's fundamentals compare to other crypto projects in 2025?

What is DOLO's compliance and regulatory risk in the DeFi lending market?

How will Solana SOL price volatility evolve in 2026: support resistance levels and market predictions

What is On-Chain Data Analysis: How to Track Active Addresses, Transaction Volume, and Whale Movements

What is Bitcoin market overview and why Bitcoin price dropped 1.17% in 24 hours at $90,205 USD

How Long Does It Take to Receive Bitcoin on Cash App
