What is a token economic model: distribution, inflation, and governance explained
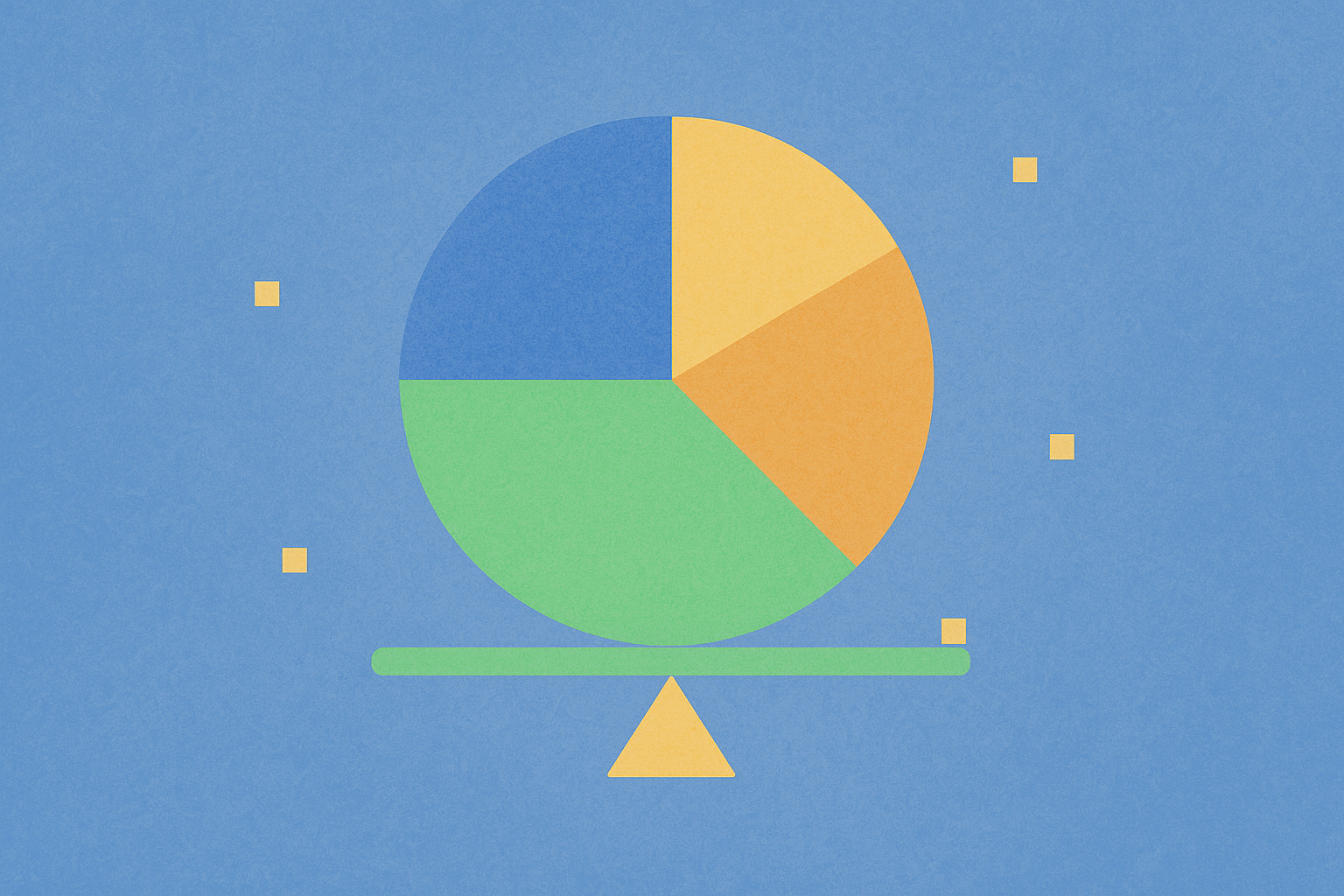

Strategic Token Distribution: 100 Billion ONDO Allocated Across Team (20%), Ecosystem (52.1%), Investors (12.9%), and Community (2.0%)
Understanding how tokens are strategically allocated reveals the core mechanics of modern blockchain economics. ONDO's token distribution model demonstrates this principle through its carefully structured allocation framework that balances multiple stakeholder interests. The ecosystem receives the largest portion at 52.1%, reflecting Ondo Finance's focus on expanding real-world asset tokenization and building protocol infrastructure. This substantial ecosystem allocation enables the platform to incentivize developers, liquidity providers, and ecosystem partners, directly supporting the growth of tokenized financial products.
The team allocation of 20% remains competitive within the industry while demonstrating measured founder retention. Notably, Ondo core team members face a 5-year lock-up period, aligning long-term interests with protocol success and reducing immediate selling pressure. The investor allocation of 12.9% reflects capital raised during development stages, while the modest 2% community allocation focuses on targeted incentive programs. The structured vesting schedule, which commenced with the January 18, 2026 token unlock, prevents supply flooding and gradually distributes tokens across the market. This measured approach to token economics shows how distribution decisions directly influence market dynamics, governance participation, and ecosystem development—essential components of any sustainable tokenomics model.
Controlled Supply Mechanism: Fixed 100 Billion Cap with 31.6 Billion Circulating and Strategic Linear Unlock Schedule to Prevent Market Volatility
Ondo Finance implements a disciplined supply framework designed to minimize market disruption through its token architecture. The project maintains a fixed 10 billion token cap, with 3.159 billion currently circulating—representing approximately 31.59% of total supply. This deliberate circulation ratio reflects a carefully orchestrated vesting structure that staggers token releases over time, preventing sudden supply shocks that typically trigger volatility.
The strategic unlock schedule follows a linear distribution pattern, with major releases tied to specific milestones and ecosystem needs. The upcoming January 18, 2026 unlock exemplifies this approach, releasing 1.94 billion tokens allocated between protocol development (825 million) and ecosystem growth (792 million). Rather than concentrating tokens among single stakeholders, Ondo distributes new supply across multiple segments, reducing concentrated selling pressure.
This controlled release mechanism directly addresses market volatility concerns inherent in cryptocurrency token economics. By maintaining predictable unlock timing and transparent allocation details, the project allows market participants to price in expected supply additions rationally. The vesting schedule's architecture—splitting releases between community and development initiatives—further distributes selling pressure across different holder motivations and time horizons. Such methodical supply management represents a sophisticated approach to token distribution economics, enabling sustainable growth while protecting existing holders from unanticipated dilution events.
Deflation Through Destruction: Token Burning Strategy to Reduce Circulating Supply and Enhance Long-term Value Stability
Token burning serves as a deliberate deflationary mechanism that permanently removes tokens from circulation, creating artificial scarcity that can enhance long-term value stability. When projects implement token burning strategies, they systematically eliminate a portion of their supply, reducing the total tokens available in the market. This approach counters inflation pressures and helps prevent excessive supply dilution that would otherwise depress asset value over time.
Real-world applications demonstrate how structured token management addresses supply concerns. Ondo Finance, for example, manages its token economics through a carefully timed vesting schedule rather than immediate full distribution. With a 57% unlock of its total supply scheduled for January 2026, the project strategically phases token releases across multiple years. This method—totaling 1.94 billion tokens worth significant market value—mitigates the shock of massive supply increases that could otherwise trigger severe price volatility.
By controlling when tokens enter circulation, projects effectively implement deflation principles that maintain economic equilibrium. The gradual release combined with potential burning mechanisms reduces sudden supply shocks and helps stabilize token value during critical market periods. This carefully balanced approach demonstrates how token economics models integrate deflation strategies to protect long-term holder value while managing liquidity responsibly.
Multi-Dimensional Governance Utility: ONDO Holders Gain Voting Rights, Staking Rewards, Fee Discounts, and Protocol Decision-Making Authority
ONDO holders leverage a comprehensive governance framework that directly aligns token ownership with protocol influence and economic rewards. By staking ONDO tokens within the protocol's smart contracts, holders access multiple value streams simultaneously—earning staking rewards while gaining voting rights and fee discounts on transactions. This multi-layered incentive structure ensures that governance participation remains economically attractive and creates meaningful reasons for token holders to engage actively in protocol decisions.
The governance process itself operates through a structured two-stage mechanism designed to ensure thoughtful decision-making. Proposals begin on the Flux Finance Governance Forum, where community members discuss potential changes to economic parameters and smart contract upgrades. Once a proposal is refined, holders with sufficient voting power—determined through a 100,000,000 ONDO threshold—submit it for binding on-chain voting. The DAO infrastructure, forked from Compound's Governor Bravo and managed through Tally, facilitates this voting process transparently and securely. Successful proposals execute after a predetermined delay period, allowing stakeholders time to evaluate implications before implementation.
Beyond voting, staking ONDO represents an active strategy to capture protocol revenue, particularly from liquidations. This economic model ensures that governance participants benefit directly from protocol success and health, creating natural alignment between individual token holder incentives and protocol objectives. Fee discounts further reward engaged stakeholders, making long-term governance participation economically rational within the token's broader economic structure.
FAQ
What is a Token Economic Model (Token Economic Model)? Why is it important for blockchain projects?
A token economic model is a system that manages resource allocation and incentivizes participant participation in blockchain projects. It is crucial because it ensures fair distribution, sustainable growth, and aligns stakeholder interests through transparent incentive mechanisms and governance structures.
What is token distribution mechanism? How are tokens typically allocated to founders, investors, community, and ecosystem?
Token distribution typically allocates 15-25% to founders, 20-30% to investors, 30-40% to community, and 15-25% to ecosystem development. This structure balances development incentives, liquidity, and community engagement for sustainable growth.
What is token inflation? How to design a reasonable inflation rate to balance incentives and value stability?
Token inflation is the rate of increase in token supply. A reasonable inflation rate should balance ecosystem incentives with price stability. Lower inflation preserves value, while strategic emissions reward participants and maintain network security. Optimal rates typically range from 2-10% annually, adjusted based on network maturity and adoption.
What does token governance mean? How do token holders participate in project decisions and voting?
Token governance means decision-making power is held by token holders. They vote on new features, token issuance, fee adjustments, and budget allocation. This ensures projects develop according to holder interests.
What is the role of vesting (锁仓期) in a token economic model?
Vesting delays token unlocking, aligning team incentives with long-term project success. It prevents immediate token dumping, stabilizing market price. It ensures founders and core contributors retain tokens, promoting commitment and reducing selling pressure from early stakeholders.
How to assess whether a token economic model design is reasonable and sustainable?
Evaluate four key dimensions: token supply (control inflation/deflation), token utility (real use cases and demand), token distribution (fair allocation and lock-up schedules), and governance (staking mechanisms and incentives). A sustainable model balances supply constraints, increases demand, and maintains long-term ecosystem growth.
What is the relationship between token economic model and project long-term value?
Token economic model directly determines project long-term value. Rational distribution mechanism builds community trust and sustainability. Controlled inflation supports stable growth. Strong governance ensures aligned incentives for all stakeholders.
Common token distribution pitfalls and how to avoid them?
Key pitfalls include imbalanced allocation where team and investors hold over 60% of tokens, and short unlock periods causing sudden sell-offs. Avoid these by ensuring fair distribution across stakeholders, implementing gradual unlock schedules, and maintaining transparent vesting mechanisms for long-term sustainability.

Understanding Sybil Attacks: Enhancing Security in Blockchain Networks

Top DAO Crypto Initiatives for New Enthusiasts

What Are the Compliance and Regulatory Risks in DeFi and Crypto Exchanges in 2025?

Understanding Decentralized Autonomous Organizations in Cryptocurrency

What Is Tokenomics: Token Distribution, Inflation Mechanisms, and Burn Strategies Explained
What Is a Token Economics Model and How Do Allocation, Inflation, and Governance Work?

What is Spot and Futures in Crypto

Solana vs Ethereum, XRP & Cardano: Complete Comparison Guide

How to Buy Algorand
How Many People Own 2 Bitcoin: Exploring Ownership

When Will Crypto ETFs Be Approved: Latest Timelines and Market Impact
