Forced Liquidation


What is Forced Liquidation?
Forced liquidation refers to an involuntary conversion of assets into cash or cash equivalents, such as stablecoins. It represents a critical risk management mechanism in leveraged trading that creates market orders to automatically exit positions when specific conditions are met. The term liquidation simply means selling assets for cash, but forced liquidation distinguishes itself by occurring automatically rather than at the trader's discretion.
In the context of cryptocurrencies, forced liquidation happens when an investor or trader is unable to fulfill the margin requirements for a leveraged position. This mechanism protects lenders and exchanges from potential losses by ensuring that borrowed funds are recovered before a position's value falls below the borrowed amount. The concept of liquidation applies to both futures contracts and margin trading across various cryptocurrency platforms.
Understanding forced liquidation is essential for anyone engaging in leveraged trading, as it directly impacts risk management strategies and can result in the complete loss of invested capital. Unlike voluntary liquidation where traders choose to close positions, forced liquidation removes control from the trader's hands, making it a critical consideration before entering any leveraged position.
How Forced Liquidation Works
When trading with leverage, the liquidation price becomes a crucial metric that requires constant monitoring. The relationship between leverage and liquidation price is inverse: the higher the leverage used, the closer the liquidation price moves to your entry point. This proximity creates a narrower margin for error and increases the risk of forced liquidation.
Let's examine a practical example to illustrate this mechanism. Suppose you start with $50 in capital and enter a leveraged long position in the BTC/USDT market with 10x leverage. Your total position size becomes $500, consisting of your $50 initial capital plus $450 in borrowed funds. If Bitcoin's price decreases by 10%, your position value drops to $450.
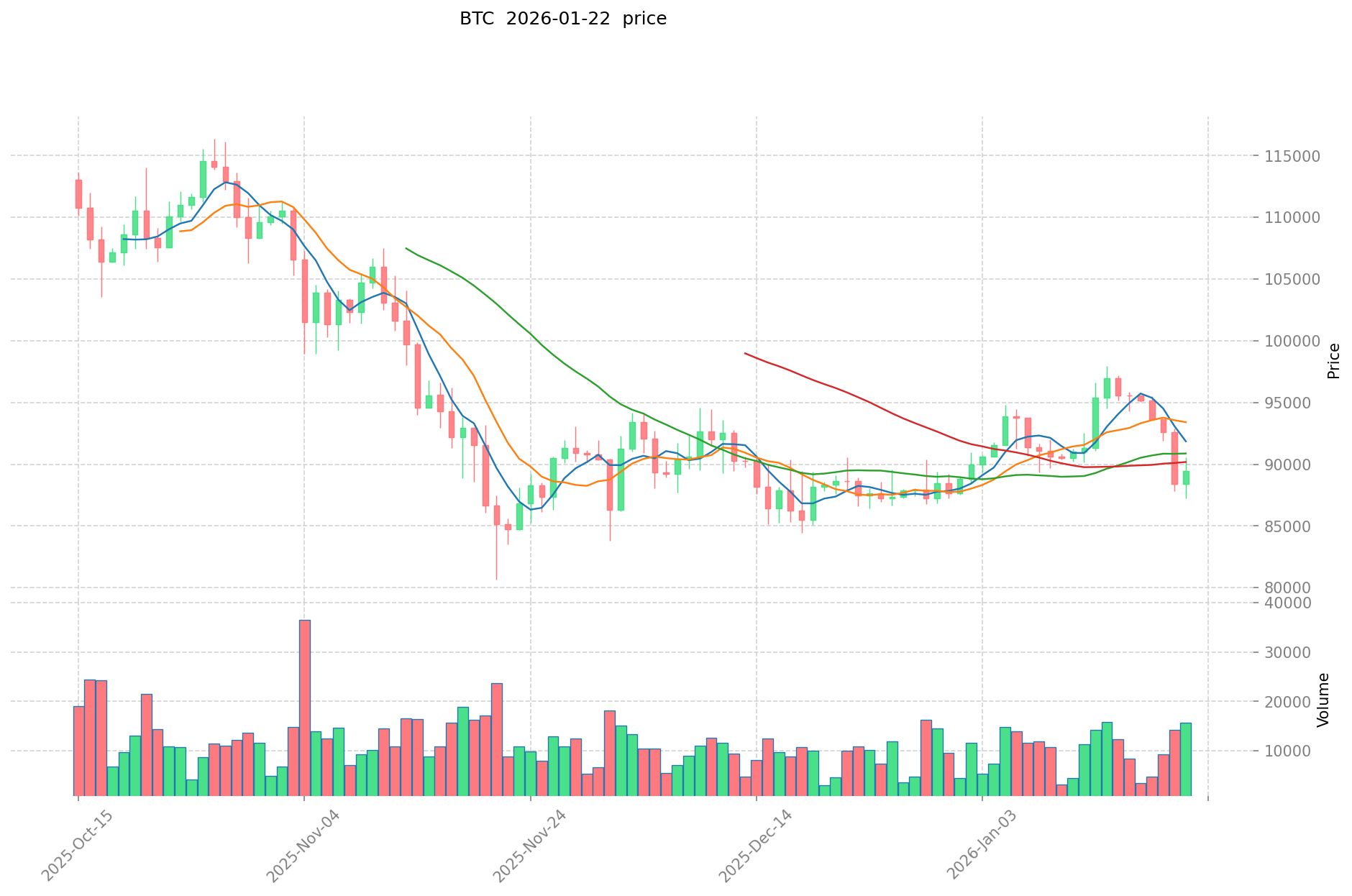 At this point, your entire initial capital has been wiped out, and any further losses would begin to affect the borrowed funds.
At this point, your entire initial capital has been wiped out, and any further losses would begin to affect the borrowed funds.
The lender of those funds, whether an exchange or other traders, will not risk incurring losses on your behalf. Therefore, they automatically liquidate your position to protect their capital. This means the position is forcibly closed, and you lose your initial investment of $50. The liquidation occurs before the borrowed funds are at risk, ensuring the lender can recover their capital.
Forced liquidation typically incurs an additional liquidation fee, which varies across different platforms. This fee exists to incentivize traders to manually close their positions before automatic liquidation becomes necessary. By closing positions voluntarily, traders can avoid these additional fees and potentially preserve more of their capital. Understanding these mechanics emphasizes the importance of proper risk management and position sizing when trading with leverage.
Calculating Liquidation Risk
Many trading platforms provide tools to help traders calculate their liquidation price before entering a position. Leading exchanges offer handy calculators that allow users to determine their potential Profit and Loss (PnL), target price, and liquidation price in advance. These tools are invaluable for risk assessment and position planning.
Calculating your liquidation price involves understanding several key factors: your entry price, leverage ratio, position size, and the maintenance margin requirements of your chosen platform. The liquidation price represents the threshold at which your position's equity falls to the maintenance margin level, triggering automatic closure. By knowing this price point beforehand, traders can make informed decisions about position sizing and leverage selection.
Risk management strategies should include setting stop-loss orders well above the liquidation price to maintain control over position exits. Additionally, traders should consider using lower leverage ratios to create a larger buffer between their entry price and liquidation price. This approach provides more room for market volatility and reduces the likelihood of forced liquidation due to normal price fluctuations.
Monitoring your position's margin ratio in real-time is equally important. Most platforms display this information prominently, allowing traders to add additional margin if their position approaches the liquidation threshold. Proactive margin management can prevent forced liquidation and preserve trading capital during volatile market conditions.
Liquidation in Traditional Finance
In more traditional financial settings, liquidation carries a broader meaning beyond leveraged trading. The term is commonly used in the context of bankruptcy procedures, where an entity is legally forced to convert their assets into liquid forms, typically cash. This process involves selling off company assets to repay creditors and stakeholders according to a predetermined priority structure.
Traditional financial liquidation differs from cryptocurrency forced liquidation in several ways. In bankruptcy liquidation, the process is typically overseen by legal authorities and follows established regulatory frameworks. The timeline is usually longer, and the process involves multiple stakeholders including courts, creditors, and bankruptcy trustees. In contrast, cryptocurrency forced liquidation occurs instantaneously and automatically based on predefined smart contract rules or exchange algorithms.
Despite these differences, both forms of liquidation share a common purpose: converting assets to cash to settle obligations and manage risk. Understanding liquidation across different financial contexts helps traders appreciate the importance of maintaining adequate collateral and managing leverage responsibly, whether in traditional markets or cryptocurrency trading environments.
FAQ
What is Forced Liquidation? How does it happen?
Forced liquidation occurs when a trader's collateral value falls below maintenance requirements. The position is automatically closed by the system to prevent further losses. It happens when asset prices drop significantly, triggering automatic position closure at market price.
Why is forced liquidation triggered? What are the specific consequences of insufficient margin?
Forced liquidation occurs when your margin ratio falls below the maintenance requirement due to unfavorable price movements. Consequences include: automatic position closure at market price, loss of remaining collateral, and account suspension until margin is restored.
How to avoid forced liquidation? What are some risk management strategies?
Maintain adequate collateral ratios above minimum requirements, set stop-loss orders, monitor positions regularly, diversify holdings, use proper position sizing, and reduce leverage during high volatility. Keep cash reserves for margin calls and adjust strategies based on market conditions.
After forced liquidation, how much loss will I incur? Do I need to compensate?
Your loss equals the difference between liquidation price and entry price. If collateral covers the debt, no additional compensation needed. Losses depend on leverage used and market movement at liquidation time.
What is the difference between forced liquidation and normal position closing?
Forced liquidation occurs when collateral value drops below maintenance requirements,automatically closing positions at market price. Normal closing is voluntary,allowing traders to exit at chosen prices with full control over timing and execution.
How is the liquidation price calculated in margin trading?
Liquidation price is calculated based on your collateral ratio and leverage. It's the price level where your position's losses equal your margin, triggering automatic liquidation. Formula: Liquidation Price = Entry Price × (1 - Collateral Ratio / Leverage). Monitor this closely to manage risk.

Leverage

Liquidation

Liquidation

Understanding Perpetual Swap Trading: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Mechanics of Perpetual Swaps
What Are the Key Security Risks and Incidents Affecting ASTER in 2025?

What is a token economic model and how do tokenomics affect crypto value

What is the difference between crypto competitors: performance, market cap, and user base comparison 2026

Bear Market

How Old is Bitcoin: A Brief History of the Original Cryptocurrency

Why is Solana Going Down
