
How does token economics model work in cryptocurrency: distribution, inflation, and governance explained
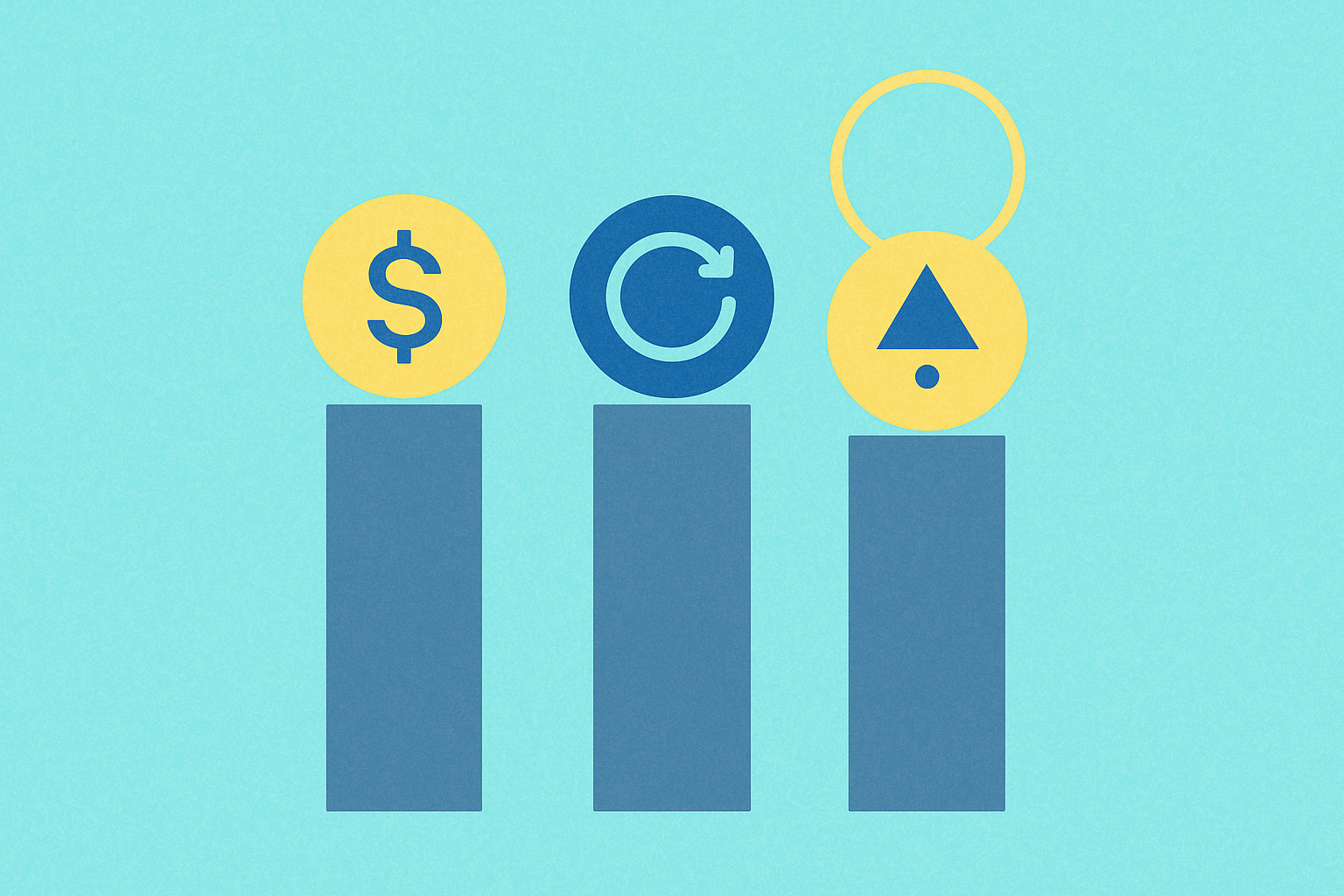


Token Distribution Strategy: 1 billion TURTLE total supply across community, ecosystem incentives, team, investors, and strategic partners
TURTLE's token distribution framework exemplifies strategic allocation within cryptocurrency token economics, spreading 1 billion tokens across five primary stakeholder categories. The ecosystem receives the largest share at 31.50%, reflecting its critical role in supporting protocol development and liquidity provisioning across partner platforms. Community engagement and airdrops collectively represent 13.90%, directly incentivizing early adopters and users to participate in the distribution protocol's growth. This allocation mechanism aligns with modern token economics principles, where community allocation drives adoption and network effects. Core contributors receive 2%, while advisors and strategic partners obtain 1.60%, ensuring experienced professionals guide protocol governance and expansion. The remaining allocation supports team operations and investor participation, creating a balanced structure that maintains incentive alignment across DeFi participants including liquidity providers, developers, and validators. This comprehensive token distribution strategy demonstrates how distribution models function as foundational components of token economics, establishing the financial incentives that coordinate behavior among protocol stakeholders and foster ecosystem sustainability. The multi-layered approach addresses different stakeholder needs while maintaining transparency and equitable participation in the protocol's tokenomics framework.
Deflationary Design Through Burning and Staking: TURTLE holders can stake tokens for governance participation and enhanced rewards in subsequent protocol versions
The deflationary mechanism for TURTLE tokens operates through a strategic combination of burning and staking mechanisms that simultaneously reduce supply and enhance holder engagement. Token holders participating in this tokenomics model convert their TURTLE into sTURTLE through staking, which serves as more than passive wealth preservation—it represents an active strategy to capture protocol revenue generated from liquidations and operational activities. This conversion process creates a direct economic incentive for governance participation, as staked token holders gain voting rights to influence protocol decisions while maintaining exposure to enhanced rewards. The governance participation structure requires sTURTLE holders to delegate their voting power, establishing clear accountability within the protocol's decision-making framework. As the TURTLE token economics evolve, subsequent protocol versions are designed to offer amplified rewards for early stakers, aligning long-term holder interests with protocol development. The burning component works complementarily with staking, systematically removing circulating tokens from the market to counteract inflationary pressures. Together, these mechanisms create a sustainable token economics model where supply contraction and governance participation reinforce each other, incentivizing token holders to remain actively engaged stakeholders rather than passive speculators in the ecosystem.
Governance Utility and Democratic Control: Token holders gain exclusive access to curated liquidity deals and voting rights in protocol development decisions
Token holders exercise direct influence over protocol evolution through structured voting mechanisms that embody democratic principles within decentralized ecosystems. When token holders participate in governance, they gain meaningful authority over critical protocol development decisions, from technical upgrades to treasury management and risk parameters. This voting power transforms passive investors into active stakeholders with genuine decision-making authority.
Beyond voting rights, governance utility often extends to exclusive access opportunities unavailable to non-token holders. The TURTLE protocol exemplifies this model by offering holders curated liquidity deals alongside governance participation, creating tangible incentives for engaged community members. These exclusive liquidity opportunities represent more than passive benefits—they reflect how governance structures align token holder interests with protocol success.
The architecture of governance utility demonstrates fundamental token economics principles in practice. By concentrating voting power among token holders, protocols ensure that economic incentives drive decision-making rather than external forces. This alignment between governance participation and exclusive benefits creates a self-reinforcing cycle: as protocols expand through successful decisions made by informed token holders, the token's utility strengthens, attracting more participants to the governance ecosystem. Such mechanisms explain why governance utility has become central to modern cryptocurrency protocol design.
FAQ
What is Token Economics (Tokenomics)? Why is it important for cryptocurrency projects?
Token economics studies how tokens operate economically, covering creation, distribution, supply, demand, and incentives. It's crucial for crypto projects because a well-designed tokenomics model ensures long-term sustainability, aligns participant interests, and determines project success through transparent, predictable rules.
What are the initial distribution methods for tokens? What are the advantages and disadvantages of ICO, airdrop, and mining distribution?
Token distribution includes ICO, airdrop, and mining. ICO raises funds through token sales but carries high risk. Airdrops distribute quickly and fairly but may lack commitment. Mining rewards computation but requires resources and time investment.
How is token inflation mechanism designed? What impact does inflation rate have on token price?
Token inflation is designed with gradual reduction in new token issuance to control inflation rates. A 2% annual terminal inflation maintains market stability and prevents excessive dilution. Reasonable inflation design promotes healthy market development and impacts token price through supply-demand dynamics.
What is token burn mechanism and how does it help control inflation?
Token burn removes coins from circulation permanently, reducing total supply. This decreases inflation by limiting token availability, increasing scarcity value and helping maintain price stability in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
What does token governance mean? How do token holders participate in project decisions?
Token governance allows holders to vote on project development and operations. Holders can decide on new features, token supply, fee adjustments, and budget allocation through voting, enabling community participation in governance.
What is the relationship between staking rewards and token economics?
Staking rewards are integral to token economics, incentivizing network participation and security. These rewards come from token inflation, aligning holder interests with protocol sustainability while reflecting market value dynamics.
How to assess whether a cryptocurrency project's token economics model is healthy and sustainable?
Evaluate token distribution fairness, inflation schedule transparency, holder concentration, governance participation rates, transaction volume trends, and long-term sustainability incentives. Healthy models show balanced distribution, controlled inflation, active governance, and strong community engagement supporting ecosystem growth.
What are the differences in token economics models between Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other mainstream cryptocurrencies?
Bitcoin's token economics model is simple, functioning purely as digital currency. Ethereum and other mainstream coins feature more complex models supporting diverse functions like smart contracts, governance, and staking mechanisms.

What Are the Key Components of a Successful Token Economic Model in Crypto?

How Does Crypto Fund Flow Affect Exchange Holdings and On-Chain Metrics?

How Does the Token Economy Model Influence Token Distribution and Governance?

How Does Crypto Fund Flow Impact Market Sentiment and Price Movements?

Explore the Comprehensive Guide to Getting Started with the DAO Kernel Protocol
How does RIVER token distribution affect exchange inflows and on-chain staking concentration

What Does a Bitcoin Look Like: A Visual Guide

What is SAFE token market overview: price, trading volume, market cap and liquidity in 2026

What is RaveDAO (RAVE) fundamentals: how does the whitepaper logic, NFT utility, and $3 million revenue drive the token's value
What is Hyperliquid (HYPE) fundamentals analysis: whitepaper logic, use cases, and technology innovation explained

What is Hyperliquid (HYPE) market overview? Current price $26.03, market cap $7.86B, and 24-hour trading volume explained
