Optimizing Blockchain Data Structures: Exploring Verkle Trees
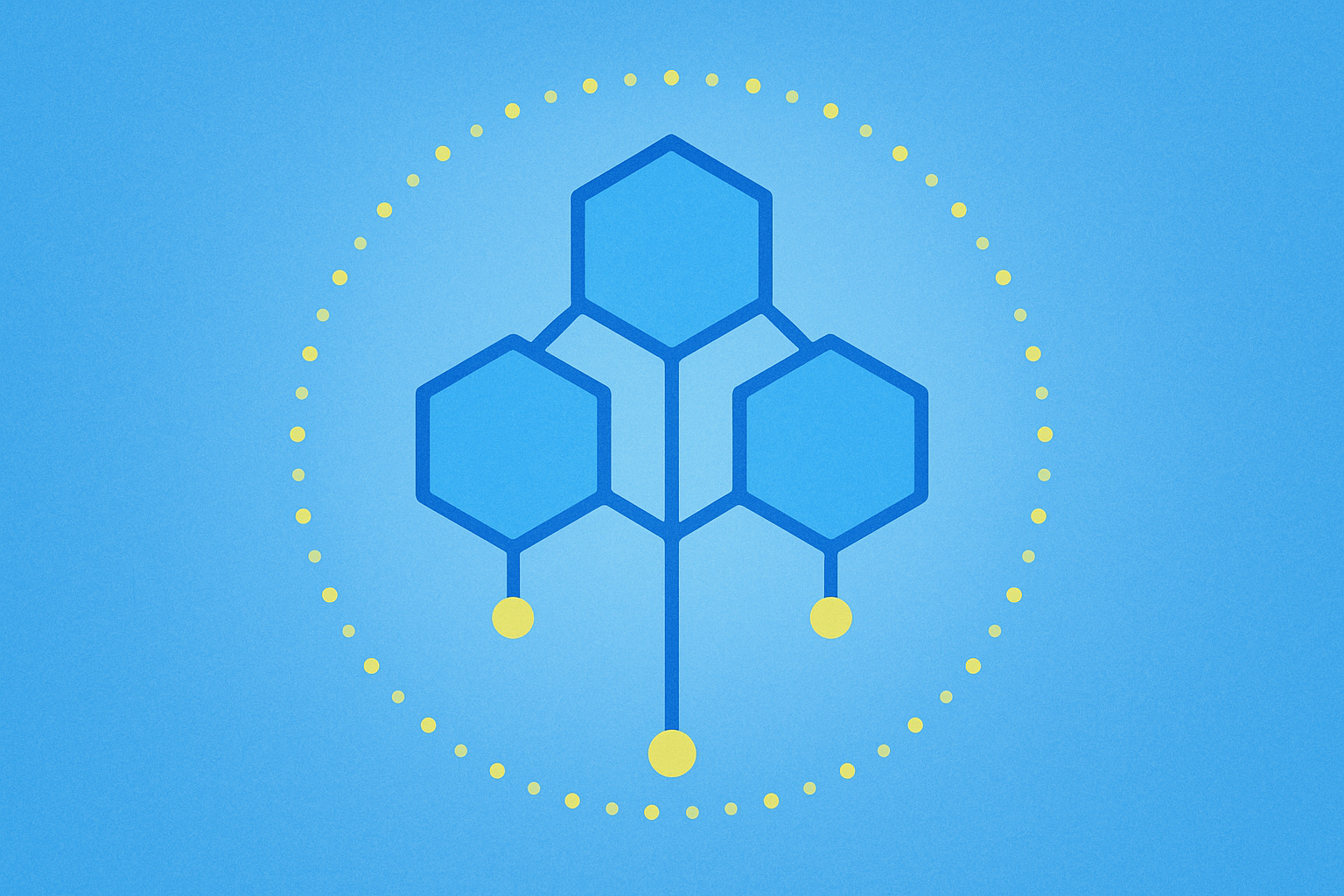
What are Merkle trees and how do they enable Proof of Reserves?
In the world of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency, understanding the fundamental mechanisms that ensure data integrity and security is crucial. Two key concepts—Merkle trees (also known as Verkle trees in their more advanced implementation) and Proof of Reserves—play vital roles in maintaining transparency and trust in decentralized systems. This article explores these concepts in depth, explaining how they work together to provide verifiable proof of asset holdings in cryptocurrency platforms.
First, what's a "hash"?
A hash is a fundamental building block of blockchain technology. It is a unique, immutable sequence of both numbers and letters that is generated by a data set of any length and size. In blockchain contexts, this data set can theoretically be infinite, making hashes incredibly versatile for securing information.
The process works through a cryptographic hash function, which transforms input data into a fixed-length string of characters. When a new block is added to a blockchain, it is cryptographically linked to the existing block before it through this hash function. The function generates transaction data from a block into a unique string of text—the hash—that cannot be altered without also changing the preceding block's hash value and, consequently, the entire history of the blockchain.
One of the most important properties of hashes is their sensitivity to changes. Altering any part of the data set, no matter how small, will completely alter its hash. This one-way transformation means that once data is converted into a hash, it cannot be reverse-engineered to reveal the original source data. This mechanism is what makes blockchains "cryptographic" and ensures that data input remains secure against decryption attempts.
The cryptographic hash function is the foundation that allows blockchains to be immutable and tamper-proof. Every block is intrinsically tied to the blocks that came before and after it, creating an unbreakable chain of verified information. In practical terms, a Transaction Hash (Tx Hash) serves as a unique identifier generated by a cryptocurrency transaction, proving that the transaction was validated and added to the blockchain.
Then what's a Merkle Tree?
Patented by Ralph Merkle in 1979, a Merkle Tree is essentially a hash "tree" structure that revolutionized how data verification works in distributed systems. This innovative data structure, which has evolved into more advanced forms like Verkle trees, addresses a critical challenge in decentralized, peer-to-peer networks: how to efficiently verify the consistency of transactions across all participating networks.
Without a transaction hash function like a Merkle Tree or Verkle trees, networks would need to continuously validate all transactions on the blockchain, which would be tremendously inefficient and impractical as the blockchain grows. To understand this concept better, consider an analogy of running an ice cream shop. When calculating January's profit and loss totals using pen and paper, discovering an input error on January 5th would require recalculating all subsequent entries through the end of the month—a daunting and inefficient process.
A cryptographic hash function, in this analogy, works similarly to Excel or accounting software, where updates to any numerical input automatically change the totals in real time without manually altering the rest of the balance ledger. However, instead of altered numerical inputs changing numerical totals, the transaction hash (Tx Hash) changes to a different randomized sequence to reflect modifications to transactions on the blockchain.
Merkle trees and their advanced variants like Verkle trees function like sophisticated password generators, converting data into randomized alpha-numerical sequences (hashes) that link to corresponding transactions on the blockchain. This creates a hierarchical hash "tree" structure. The beauty of Merkle trees and Verkle trees lies in their ability to quickly verify data transferred between computers in a peer-to-peer network by ensuring that blocks sent between peers are received unaltered and undamaged.
The structure of a Merkle Tree consists of leaves or leaf nodes, which are the hashes representing blocks of data, such as individual transactions on a blockchain. Nodes toward the top of the tree are hashes of their respective children. For example, Hash 1 would be the combination of the two hashes below it on the tree: Hash 1 = Hash (hash 1-0 + Hash 1-1). This hierarchical structure continues upward until reaching the very top of the tree, where the Top Hash (also called the root) resides.
The Top Hash is particularly important because it allows any part of the hash tree to be received from untrusted sources, such as peer-to-peer networks. When a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, it can be checked against the trusted top hash for verification, determining whether the hash has been damaged or falsified by a malicious actor. Instead of sending entire files over the network, systems can send just a hash of the file and check it against the Top Hash to verify its integrity. This mechanism is partly what defines cryptocurrency as a "trustless" system, where verification doesn't require faith in any central authority. Verkle trees further enhance this efficiency by reducing proof sizes and improving verification speeds.
What are Proof of Reserves?
In traditional financial accounting, record systems consisting of ledgers, records, and balance sheets are reviewed and verified by third-party auditors. If discrepancies are found, they are flagged and must be resolved before the auditor validates the books. However, decentralized platforms operate without third-party auditors or humans manually balancing incoming and outgoing transactions, raising important questions about trust and transparency.
For users depositing cryptocurrency on trading platforms, a fundamental question arises: How can you verify that your deposit is still there days, months, or years later? How can you trust that the platform isn't using your deposited funds for other purposes? While blockchain explorers exist, history has proven they aren't always transparent enough to protect against bad actors.
Driven by the desire to alleviate customer concerns about crypto funds held in centralized platforms, many major cryptocurrency exchanges have launched Proof of Reserves protocols. Proof of Reserves is a comprehensive report of crypto assets that ensures the custodian holds the assets it claims to hold on behalf of its users.
The implementation uses the Merkle tree (hash tree), including advanced implementations like Verkle trees, to prove this claim in two distinct ways. First, individual users can find their balance in the tree and prove their assets are held within the total platform balance. This provides personal verification that their specific deposits are accounted for. Second, the total platform balance is compared to the publicized on-chain wallet balance to determine Proof of Reserves, providing system-wide verification.
By utilizing the Merkle Tree and Verkle trees to display immutable transaction data and demonstrate that the data hasn't been tampered with through cryptographic hashing mechanisms, platform customers can rest assured that their assets are held on a 1:1 basis. This means that for every unit of cryptocurrency shown in a user's account balance, there is an equivalent unit held in reserve by the platform.
Conclusion
Merkle trees, Verkle trees, and Proof of Reserves represent critical innovations in cryptocurrency security and transparency. Hashes provide the foundational cryptographic security that makes blockchains immutable and tamper-proof, while Merkle trees and their advanced implementations like Verkle trees offer an efficient method for verifying data integrity across distributed networks without requiring continuous validation of all transactions. Building upon these technologies, Proof of Reserves protocols give cryptocurrency users verifiable assurance that trading platforms actually hold the assets they claim to hold on behalf of their customers. Together, these mechanisms address fundamental trust issues in decentralized finance, transforming cryptocurrency platforms from systems requiring blind faith into transparent, verifiable platforms where users can independently confirm the security and availability of their assets. As the cryptocurrency industry continues to evolve, such transparency mechanisms have become increasingly important for building and maintaining user trust in digital asset platforms.
FAQ
What is a verkle tree?
A verkle tree is an advanced data structure in blockchain that efficiently manages and verifies large amounts of transaction data. It improves upon Merkle trees, offering enhanced scalability and security for blockchain networks.
What is the difference between Merkle tree and Verkle tree?
Merkle trees ensure data integrity, while Verkle trees enhance blockchain scalability by reducing computational and storage needs.
What is a hash tree also called?
A hash tree is also called a Merkle tree. It's a data structure that efficiently verifies large data sets.
What is a Merkle tree used for?
Merkle trees are used for efficient data verification in large datasets, ensuring data integrity in blockchain networks, and optimizing data synchronization in distributed systems.

Exploring Plonky2 and the Future of Zero-Knowledge Proofs

Exploring Fraud Proof Mechanisms in Layer 2 Blockchain Solutions

TPS là gì?
Uncovering StarkNet: Understanding Cairo

Enhancing Cross-Chain Connectivity with Advanced Bridge Solutions

What is Layer 2

How does Federal Reserve policy and inflation data affect cryptocurrency prices

What is PYUSD? The PayPal Stablecoin Going Global

What is the impact of regulatory compliance and SEC oversight on crypto market adoption in 2026

What is the difference between top crypto competitors in 2026: market cap, performance, and user adoption compared

How Can You Measure Crypto Community Activity and Ecosystem Growth in 2026
