What is a token economics model and how does crypto distribution, inflation design, and governance mechanisms work

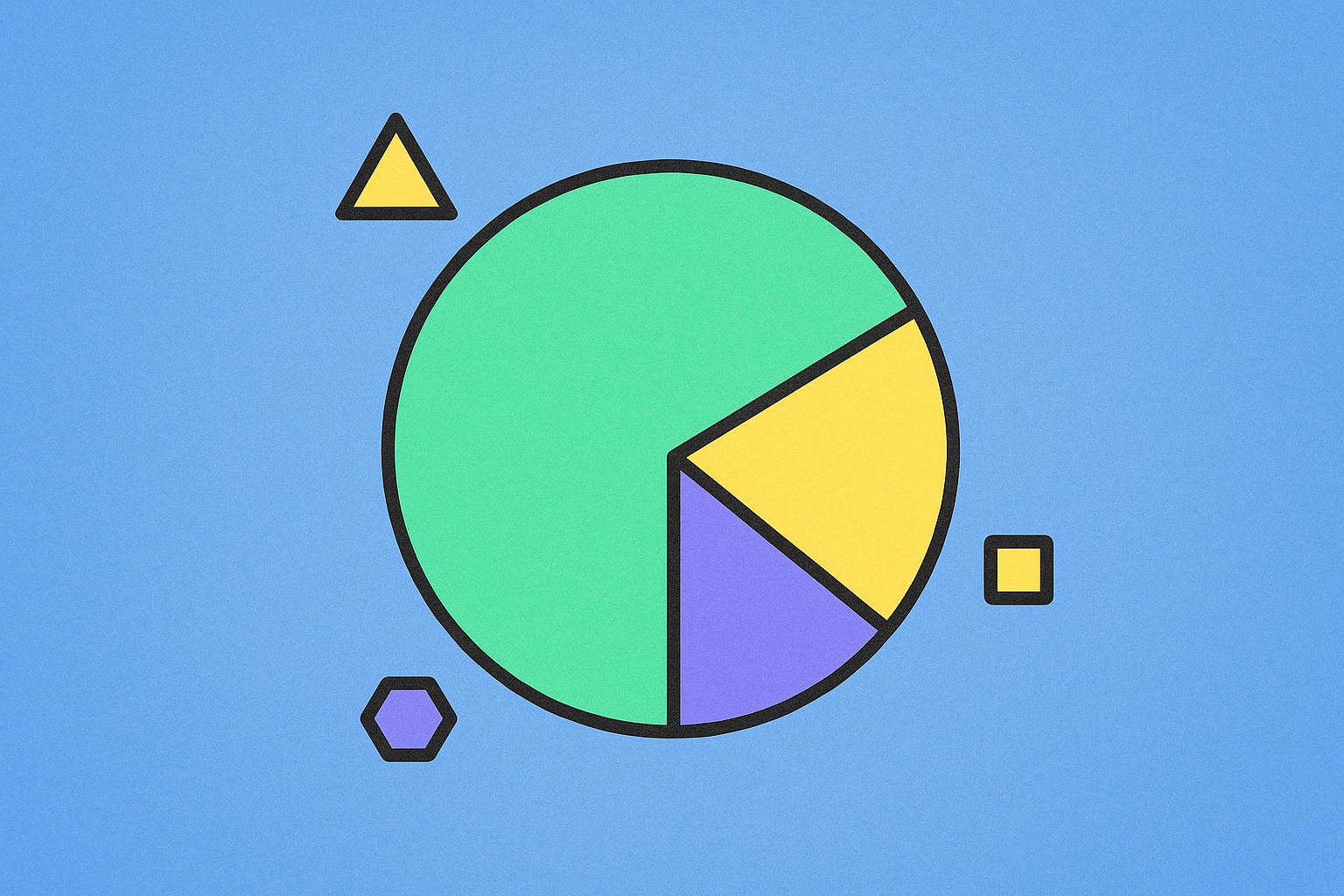
Token Distribution Framework: Analyzing Team, Investor, and Community Allocation Ratios
A well-designed token distribution framework serves as the foundation of healthy token economics, determining how newly created tokens are allocated among different stakeholder groups. This allocation structure significantly influences project longevity, investor confidence, and community engagement, making it one of the most critical decisions in crypto distribution strategy.
Effective token distribution typically divides allocations among three primary categories, each serving distinct purposes in the ecosystem. Team allocations generally comprise 15-25% of total supply, incentivizing long-term project development while ensuring developer commitment. Investor allocations, typically 20-30%, provide capital for infrastructure and marketing, with early investors often receiving favorable terms reflecting their risk exposure. Community allocations usually represent 40-50% of supply, reserved for ecosystem participants, users, and decentralized governance initiatives.
The ratios between these allocation segments reflect project philosophy and sustainability goals. Projects emphasizing decentralization often skew toward higher community percentages, while infrastructure-heavy projects may allocate more to teams. Vesting schedules further refine distribution frameworks by releasing tokens gradually over years rather than immediately, preventing supply shocks and aligning stakeholder interests with long-term success. Understanding these allocation dynamics is essential for evaluating any tokenomics model, as imbalanced distributions frequently correlate with poor token performance and reduced governance participation within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Inflation and Deflation Mechanisms: Balancing Supply Growth with Value Preservation
Effective token economics requires careful calibration of supply dynamics to maintain long-term value while incentivizing network participation. Inflation mechanisms introduce new tokens into circulation through rewards for validators, stakers, or ecosystem contributors. However, unchecked inflation erodes token value, which is why sophisticated supply management has become essential for mature cryptocurrency projects. Many projects implement deflationary mechanisms such as token burns, staking rewards that reduce circulating supply, or transaction fees that remove tokens from the market. Polygon's ecosystem token, for instance, operates with unlimited maximum supply, requiring active supply management strategies to prevent dilution. The balance between inflation and deflation directly impacts token holder returns and network security incentives. Projects often employ tiered inflation schedules that decrease over time, reducing new supply as the network matures. Some protocols combine multiple mechanisms: inflation rewards early adopters and developers while deflation through burns or treasury management preserves value for existing holders. This dual approach addresses the fundamental tension between growing the network economically and maintaining stable token value. Understanding these mechanics helps investors evaluate how a project's supply design affects long-term viability and token appreciation potential.
Burning Strategies and Token Circulation: Reducing Supply to Support Price Stability
Token burning serves as a fundamental mechanism within token economics models, directly influencing supply dynamics and market value. When projects permanently remove tokens from circulation, they create deflationary pressure that can support price stability by reducing available supply. This practice reverses traditional inflationary pressures inherent in many cryptocurrency protocols.
The mechanics of burning strategies vary across projects. Some implement automatic token destruction through protocol fees, transaction costs, or governance decisions. Others conduct periodic manual burns triggered by specific milestones or community votes. These burning strategies work in tandem with inflation design to maintain equilibrium in token circulation. For example, Polygon's token economics incorporates supply management mechanisms as part of its broader Polygon 2.0 framework, demonstrating how burning fits into larger governance structures.
Effective burning strategies require careful calibration to avoid excessive deflation while maintaining incentive structures. When token circulation decreases through burning, holders experience potential appreciation, though sustainable price stability depends on genuine utility and adoption. The relationship between supply reduction and market performance isn't purely mechanical—it must align with ecosystem fundamentals and governance mechanisms that ensure long-term viability of the token economics model.
Governance Rights and Utility: Empowering Stakeholders Through Voting Power and Protocol Control
Governance rights form a cornerstone of modern token economics, transforming token holders from passive investors into active participants in protocol evolution. When tokens grant voting power, they distribute decision-making authority across the community rather than concentrating it with developers or corporations. This democratization mechanism allows stakeholders to propose, debate, and vote on critical upgrades, parameter changes, and resource allocation decisions that shape the platform's future trajectory.
Voting power typically correlates with token holdings, though weighted mechanisms can adjust influence based on factors like stake duration or governance participation history. This approach incentivizes long-term commitment while preventing governance attacks by entities with short-term interests. Holders exercising voting rights become stewards of the protocol, making decisions about feature implementations, fee structures, and treasury management.
Protocol control extends beyond voting to encompassing token holder influence over network operations. Some governance tokens enable holders to validate transactions, participate in consensus mechanisms, or manage validator selection. Others provide control over smart contract parameters, liquidity pools, or ecosystem treasury funds. This utility creates inherent demand for tokens beyond speculative trading.
Polygon's ecosystem token exemplifies this principle, with enhanced decentralization in community governance as a key Polygon 2.0 improvement. Token holders gain meaningful influence over network decisions, aligning individual interests with protocol success. When stakeholders wield genuine governance power and protocol control, tokens become instruments of collective ownership rather than mere financial assets, fundamentally reshaping how blockchain communities coordinate and evolve together.
FAQ
What is a Token Economics Model (代币经济学模型)?
Token economics model is the system design governing cryptocurrency supply, distribution, inflation rates, and governance mechanisms. It determines how tokens are created, allocated, and used within the ecosystem to ensure sustainable value and community participation.
What are the types of token distribution mechanisms in cryptocurrencies?
Token distribution mechanisms include: Initial Coin Offering(ICO), airdrop, mining rewards, staking rewards, team allocation, and treasury reserves. Each serves different purposes in incentivizing participation, decentralization, and long-term sustainability of blockchain projects.
What impact does token inflation design have on crypto projects?
Token inflation design significantly affects project sustainability. Controlled inflation incentivizes network participation and rewards early supporters, while excessive inflation erodes token value and user confidence. Optimal inflation balances ecosystem growth, stakeholder rewards, and long-term value preservation, directly influencing adoption rates and market performance.
What is the role of governance mechanisms in token economics?
Governance mechanisms empower token holders to participate in protocol decisions, including parameter adjustments, fund allocation, and strategic direction. They ensure decentralized decision-making, enhance community engagement, and align incentives between stakeholders, creating sustainable and transparent token ecosystems.
How to assess whether a cryptocurrency project's token economics model is reasonable?
Evaluate token distribution fairness, inflation rate sustainability, governance decentralization, and use case utility. Analyze vesting schedules, founder allocation, community incentives, and whether tokenomics aligns with project fundamentals and long-term value creation potential.
Why is Token Vesting (代币解锁计划) important?
Token vesting prevents sudden supply flooding and price crashes. It aligns team incentives with long-term project success, builds investor confidence through gradual release, and ensures sustainable tokenomics by controlling inflation and maintaining healthy market dynamics.

Understanding Sybil Attack Prevention in Cryptocurrency

What is tokenomics model: how does token distribution, inflation design, and governance mechanisms work

Secure and Scalable Enterprise Blockchain Solutions for Businesses

What is token economics model: a complete guide to token allocation, inflation design, and governance in 2025

What is a Token Economic Model: Distribution, Inflation, Burning Mechanisms & Governance Rights Explained
How to Measure Cryptocurrency Community and Ecosystem Activity: Social Media Following, Developer Contributions, and DApp Growth

Why Is XRP Not Moving: An In-Depth Analysis

Haha Money Printer Go Brrrrr
What is the Golden Pocket in Trading?

X Empire Listing Price After Token Launch and Airdrop

Which Banks Use XRP in Their Operations
