What is token economics model: distribution, inflation, and governance explained
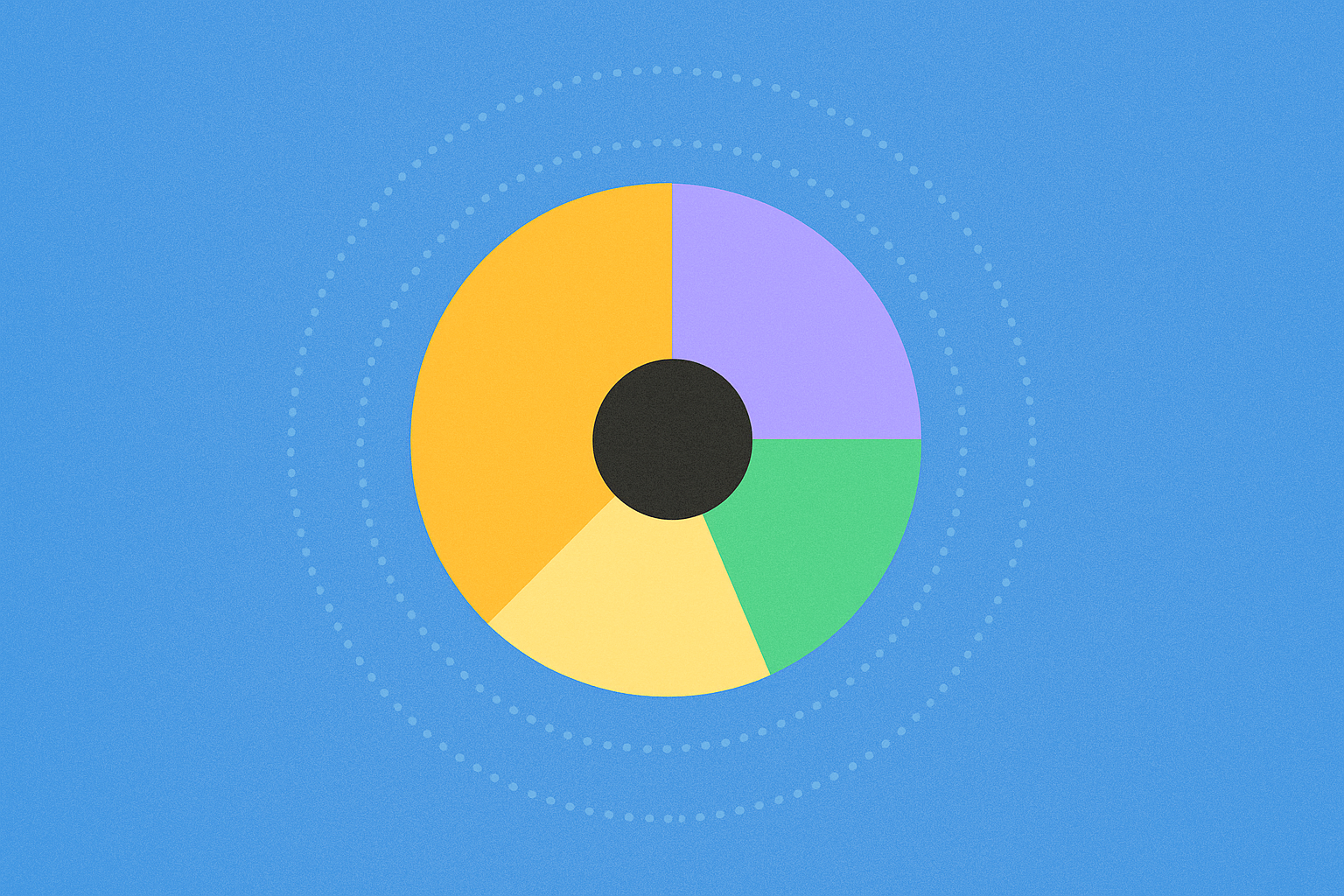
Token Distribution Structure: 51.02% Community, 16.5% Foundation, 13.48% Investors, and 19% Core Contributors
The Aptos token economics model demonstrates a carefully balanced allocation structure designed to align incentives across multiple stakeholder groups. This distribution approach ensures that network participants—from individual users to institutional investors—have meaningful ownership stakes and governance participation rights.
The allocation breaks down strategically across key constituencies. Community members receive the largest share at just over half, reflecting a commitment to decentralization and broad participation. Foundation reserves support long-term ecosystem development and grants. Investor allocations reward early backers, while core contributor tokens compensate the team building the infrastructure.
| Stakeholder Group | Allocation | Token Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Community | 51.02% | 510.2M APT |
| Core Contributors | 19% | 190M APT |
| Foundation | 16.5% | 165M APT |
| Investors | 13.48% | 134.8M APT |
This token distribution structure reflects modern blockchain governance principles where community empowerment drives adoption. The vesting schedule further reinforces long-term alignment—community and foundation tokens unlock over 120 months with cliff periods, while investor and contributor allocations follow 35-month schedules. Such token economics models prevent sudden market flooding while creating predictable supply dynamics that influence tokenomics sustainability.
Inflation and Staking Economics: APY declining from 7% to 3.25% annually with over 82% of tokens staked
Aptos's staking economics demonstrate a deliberate token economics design where yield incentives adjust as network participation matures. The APY reduction from 7% to 3.25% reflects a strategic shift in how inflation is distributed across the protocol. This decline isn't arbitrary but rather a programmed mechanism that recalibrates rewards as staking participation reaches critical mass.
| Metric | Initial | Current |
|---|---|---|
| Annual APY | 7% | 3.25% |
| Token Participation | Lower | Over 82% |
With over 82% of tokens staked, the network has achieved exceptional validator participation, indicating strong confidence in Aptos's proof-of-stake mechanism. This high staking participation rate fundamentally alters the inflation dynamics—fewer tokens remain in circulation, and the reduced APY maintains sustainable inflation control while still rewarding committed network participants.
The declining yield structure serves a crucial purpose in token economics governance. As inflation pressures ease with high staking participation, lower APY rates prevent excessive token dilution while maintaining network security through economic incentives. This progression shows how modern blockchain protocols balance immediate staking rewards against long-term tokenomics sustainability, demonstrating sophisticated inflation management that protects token value as the network matures.
Vesting Schedule and Supply Release: 10-year monthly unlocks for community/foundation tokens and 4-year vesting for team/investor allocations
A well-designed vesting schedule determines how tokens transition from locked to circulating supply, balancing ecosystem growth with stakeholder incentives. Different participant groups typically receive tokens on distinct timelines to align interests and manage supply dynamics strategically.
Long-term holders like foundations and community members often face extended lock periods. For example, foundation and community token allocations typically follow a 120-month linear unlock structure, releasing tokens proportionally over a decade. This extended vesting schedule ensures stable, predictable supply release while maintaining confidence in long-term project commitment. Community tokens account for substantial portions of total supply—often 40-50% of allocations—making their gradual unlock critical to preventing sudden market oversupply.
Team members and early investors generally have shorter but more complex vesting arrangements. A standard 4-year vesting period with cliff structures is common, where tokens remain fully locked during an initial period before accelerating releases. This typically includes a nonlinear schedule where approximately 80% of tokens unlock over 35 months, versus linear vesting's steady monthly disbursement.
These differentiated timelines create predictable unlock events that market participants monitor closely. When major supply release dates approach—such as quarterly or monthly token unlocks—trading volumes often increase as stakeholders position for potential price impacts. Understanding each allocation category's vesting timeline helps investors anticipate circulating supply changes and their broader token economics implications.
Governance Rights and Ecosystem Incentives: APT as governance token enabling protocol participation and ecosystem growth funding
APT serves as the governance token that empowers Aptos ecosystem participants to directly influence protocol evolution and secure the network. When APT holders stake their tokens, they unlock voting power to participate in governance proposals that shape the platform's future development, treasury allocation, and protocol upgrades. This staking mechanism extends beyond governance—it simultaneously activates reward multipliers and points accumulation, creating a dual incentive structure where active participants benefit both from protocol governance participation and financial returns.
The governance framework aligns diverse stakeholder interests through tokenized voting rights. APT validators stake tokens to participate in consensus mechanisms while simultaneously gaining governance influence, ensuring security remains coupled with decentralized decision-making. The ecosystem growth funding operates through targeted incentive programs that distribute APT grants to developers, projects, and applications building within the Aptos ecosystem. This strategic allocation of governance tokens cultivates ecosystem development by rewarding innovation and protocol participation.
Stakers employing longer lock durations achieve higher multipliers, creating an economic incentive structure that rewards long-term commitment to the protocol. This tiered approach encourages diverse participation levels—conservative participants can claim and stake APT with flexible terms, while aggressive participants maximize governance influence and rewards through extended commitment. The governance token ultimately transforms APT holders into active protocol participants rather than passive investors, integrating economic incentives with participatory governance that drives ecosystem growth and network security.
FAQ
What is a token economics model? Why is it important for blockchain projects?
Token economics model defines how tokens are created, distributed, and incentivized within a blockchain project. It's crucial because it determines token value, user participation, and long-term project sustainability. Strong tokenomics significantly increases a project's chances of success and adoption.
What are the main types of token distribution mechanisms? What impacts do different distribution methods have?
Token distribution mainly includes pre-mining and fair launch models. Pre-mining allocates tokens to early investors and teams before public release, affecting market trust and fairness. Fair launch aims to minimize early favoritism, promoting more equitable community participation and long-term price stability.
What is token inflation? How to design a reasonable inflation rate to balance project sustainability and token holder interests?
Token inflation gradually increases token supply to incentivize development and participation. A reasonable inflation rate balances sustainability and holder interests by controlling emission speed and supply caps to avoid excessive dilution while maintaining long-term value.
What does token governance mean? How do holders participate in project decisions through governance?
Token governance grants decision-making power to holders. Holders vote on key proposals affecting project development, from protocol upgrades to treasury allocation. Governance tokens enable community participation, ensuring decentralized decision-making and collective project direction.
What is the difference between fixed supply and infinite supply tokenomics models?
Fixed supply tokens have limited quantity, enabling value appreciation over time and investor appeal. Infinite supply tokens adjust based on demand, providing flexibility for game balance. Fixed supply offers scarcity and stability, while infinite supply adapts to ecosystem needs dynamically.
What is the purpose of token vesting periods? Why do projects typically set lock-up periods?
Token vesting restricts token trading during specific periods, reducing market manipulation and protecting project stability. Projects implement vesting to prevent early team members and investors from dumping tokens prematurely, ensuring sustainable token distribution and long-term project health.
How to assess whether a token economics model is healthy and sustainable?
Evaluate supply stability, distribution fairness, and inflation rates. Assess community participation, governance mechanisms, and long-term utility. Monitor vesting schedules and token allocation transparency for sustainability indicators.

What is token economics model and how does it work in crypto?

What is Tokenomics? Understanding Token Distribution, Inflation Mechanisms, and Governance in Crypto

What is token economics model and how does distribution, inflation, and governance mechanisms work?
What Are the Key Components of a Token Economic Model in 2025?

Understanding Sybil Attack Prevention in Cryptocurrency

Understanding Sybil Attacks: Enhancing Security in Blockchain Networks

Permissionless Blockchain

How to Check BTC Transaction Status
What Are the Top Cryptocurrency Competitors in 2026? A Complete Competitor Benchmarking Analysis of Market Share and Performance
What Is the Daily Combo for Hamster Kombat
What is MAGIC token and how does the Treasure ecosystem's GameFi strategy drive its value