Understanding Merkle Tree Proofs in Blockchain Technology


What are Merkle trees and how do they enable Proof of Reserves?
Merkle trees represent a fundamental cryptographic technology that enables secure and efficient verification of data integrity in blockchain systems. This article explores the concept of Merkle trees and their critical role in implementing merkle tree proof mechanisms for cryptocurrency exchanges, demonstrating how Proof of Reserves establishes trust and transparency.
First, what's a "hash"?
A hash is a unique, immutable sequence of alphanumeric characters generated from a data set of any length or size through a cryptographic hash function. In blockchain technology, this data set can be virtually infinite in scope.
The hash function serves as a critical security mechanism by converting transaction data from a block into a unique string of text that cannot be altered without modifying the entire blockchain history. When a new block is added to a blockchain, it becomes cryptographically linked to the preceding block through this hash function. This creates an immutable chain where any alteration to the data set will fundamentally change its corresponding hash value.
For example, if a transaction in block 100 is modified, the hash of that block changes, which then cascades through all subsequent blocks, making tampering immediately detectable. This one-way function cannot be reverse-engineered to reveal the original source data, which provides robust security against decryption attempts.
The Transaction Hash (Tx Hash) serves as a unique identifier for each cryptocurrency transaction, providing cryptographic proof that the transaction was validated and permanently recorded on the blockchain. This mechanism ensures blockchain immutability and tamper-proof characteristics, as every block is intrinsically connected to both preceding and subsequent blocks.
Then what's a Merkle Tree?
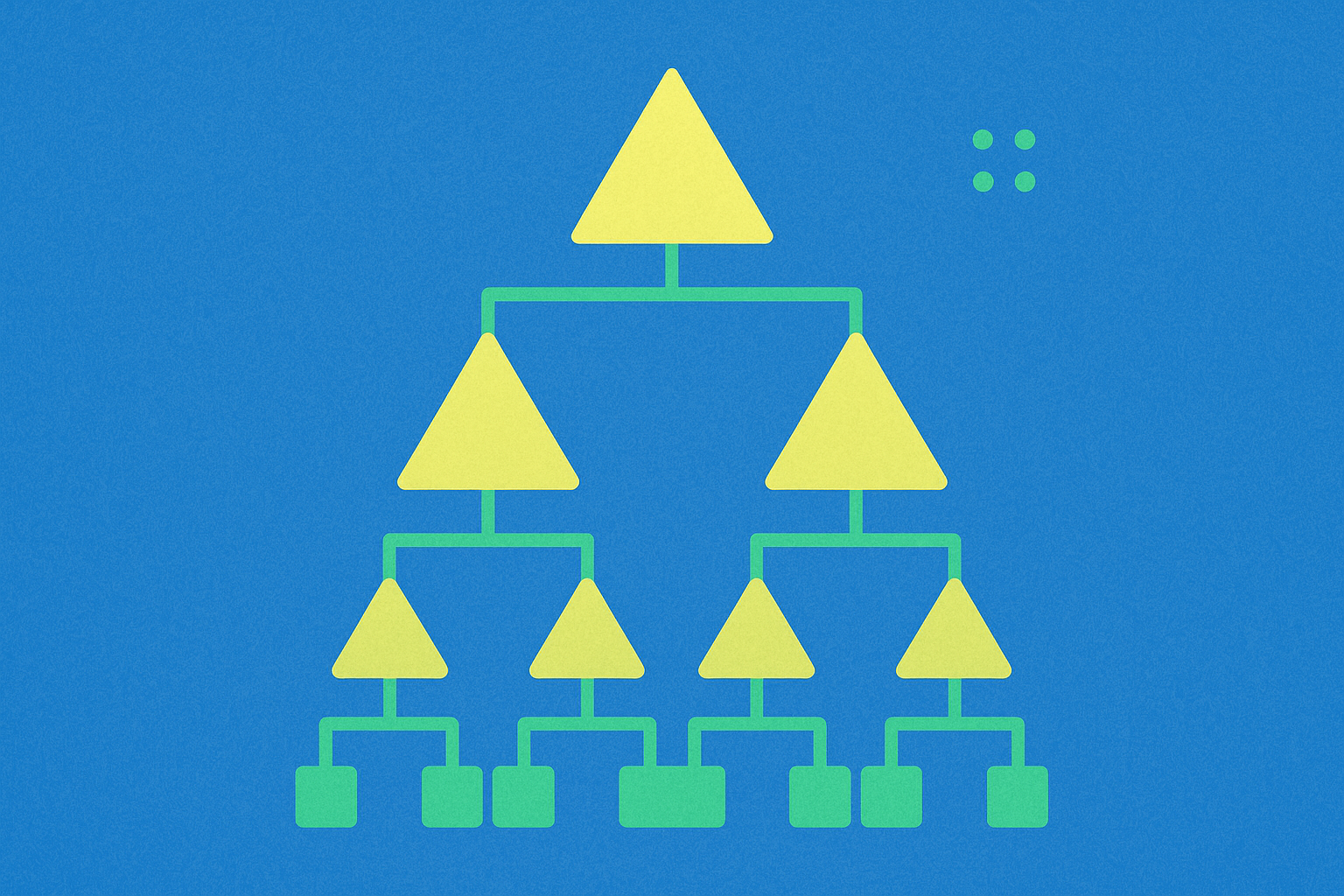
Patented by Ralph Merkle in 1979, a Merkle Tree is a hierarchical hash structure that enables efficient and secure verification of data in peer-to-peer networks. This innovative data structure solves a critical efficiency problem in blockchain technology and forms the foundation of merkle tree proof systems.
To understand Merkle trees, consider a practical analogy: imagine operating an ice cream shop and calculating monthly profit and loss statements. If you discover an error in the payment recorded for cream and sugar on January 5th, using traditional pen and paper methods would require recalculating all subsequent transactions through month-end. This approach is not only daunting but tremendously inefficient.
A cryptographic hash function operates similarly to spreadsheet software, where changes to any input automatically update related calculations without manually modifying the entire ledger. In blockchain terms, when transaction data changes, the transaction hash generates a new randomized alphanumeric sequence reflecting those modifications, creating what we call a Merkle tree.
The structure of a Merkle tree consists of leaf nodes at the bottom, which are hashes representing individual data blocks or transactions. Parent nodes higher in the tree are created by combining and hashing their child nodes. For instance, Hash 1 equals the hash of (Hash 1-0 plus Hash 1-1). This hierarchical structure continues upward until reaching the Top Hash, also called the root, which sits at the apex of the tree.
Merkle trees can quickly verify data transferred between computers in peer-to-peer networks by ensuring blocks are received unaltered and undamaged. The Top Hash enables any part of the hash tree to be received from untrusted sources and verified against the trusted root. Instead of transmitting entire files across the network, only the hash needs to be sent and checked against the Top Hash for verification. This mechanism partially defines cryptocurrency as a trustless system, eliminating the need for centralized verification authorities.
What are Proof of Reserves?
Proof of Reserves represents a transparency protocol designed to alleviate customer concerns about crypto funds held in centralized trading platforms. This system provides verifiable evidence that custodians hold the assets they claim to maintain on behalf of users through merkle tree proof methodology.
In traditional financial accounting, third-party auditors review and verify ledgers, records, and balance sheets. When discrepancies arise, auditors flag them for resolution before validating the financial books. However, decentralized platforms operate without third-party auditors or human oversight for balancing transactions.
This raises critical trust questions: How can users verify that deposits made previously remain secure? How can they trust that platforms won't misuse deposited funds? While blockchain explorers exist, history demonstrates they aren't always transparent enough to protect against bad actors.
The Merkle Tree provides a viable long-term solution through Proof of Reserves implementation. Cryptocurrency trading platforms utilize Merkle trees to demonstrate reserve holdings in two complementary ways:
First, individual users can locate their balance within the Merkle tree structure and prove their assets are included in the platform's total balance. This verification process allows users to independently confirm their holdings without relying on the platform's word alone—this is the essence of merkle tree proof validation.
Second, the total platform balance shown in the Merkle tree is compared against the publicly visible on-chain wallet balance. This comparison determines whether the platform maintains adequate Proof of Reserves, demonstrating a 1:1 backing of customer assets.
Using the cryptographic properties of Merkle trees to display immutable transaction data and prove the data hasn't been tampered with, customers gain assurance that their assets are properly secured and fully backed by actual reserves. This merkle tree proof system creates transparency without compromising security.
Conclusion
Merkle trees represent a cornerstone technology in blockchain systems, providing efficient data verification through hierarchical hash structures. By understanding how hashes create immutable data fingerprints and how Merkle trees organize these hashes into verifiable structures, we can appreciate the security and transparency they bring to cryptocurrency systems through merkle tree proof mechanisms.
The application of Merkle trees to Proof of Reserves addresses fundamental trust issues in centralized cryptocurrency platforms. This cryptographic solution enables users to independently verify their holdings while allowing platforms to demonstrate transparent reserve management without compromising individual privacy. The merkle tree proof approach ensures that every user can validate their position within the reserve structure.
As the cryptocurrency ecosystem continues evolving, Merkle trees and Proof of Reserves protocols remain essential tools for building trust and ensuring accountability in digital asset custody. The merkle tree proof methodology has become an industry standard for demonstrating solvency and maintaining user confidence.
The combination of cryptographic hash functions, Merkle tree structures, and Proof of Reserves protocols creates a trustless verification system that protects users while maintaining the decentralized principles underlying blockchain technology. This innovative merkle tree proof approach demonstrates how mathematical cryptography can replace traditional trust-based relationships with verifiable, transparent proof systems that anyone can independently audit and verify.
FAQ
What is a Merkle tree proof?
A Merkle tree proof is a set of hashes that verifies a leaf's membership in a Merkle tree. It combines sibling hashes to prove inclusion, with the root hash confirming the tree's integrity and data authenticity.
How do you verify Merkle proof?
To verify a Merkle proof, compare provided hashes against the root hash of the Merkle tree. The proof includes sibling hashes that validate each node, confirming data integrity and presence without revealing the data itself.
What is Merkle tree proof of inclusion?
A Merkle tree proof of inclusion verifies that a specific data element exists in a Merkle tree using hash values. It confirms data integrity through a series of sibling hashes leading to the root, without revealing the actual data.

Cryptography: From Ancient Ciphers to Blockchain. The Complete Guide to Information Security in the Digital Age
Introduction to Cryptography: A Beginner's Guide

Understanding Merkle Proofs in Blockchain Technology

Understanding Cryptography: Essential Concepts for Blockchain Security

Enhancing Security in Blockchain Networks with Cryptography Techniques
Understanding Merkle Proofs in Blockchain Technology
What is Fuel Network (FUEL)? Everything You Need to Know about FUEL
Zora (ZORA) Airdrop Guide: Participation Steps, Reward Collection, and Price Predictions

What Is BNB Chain?

All You Need To Know About Yescoin

How to Buy Baron ($BARRON) Coin: What is Baron Trump Cryptocurrency?
