
What is tokenomics: token distribution, inflation mechanisms, and governance explained
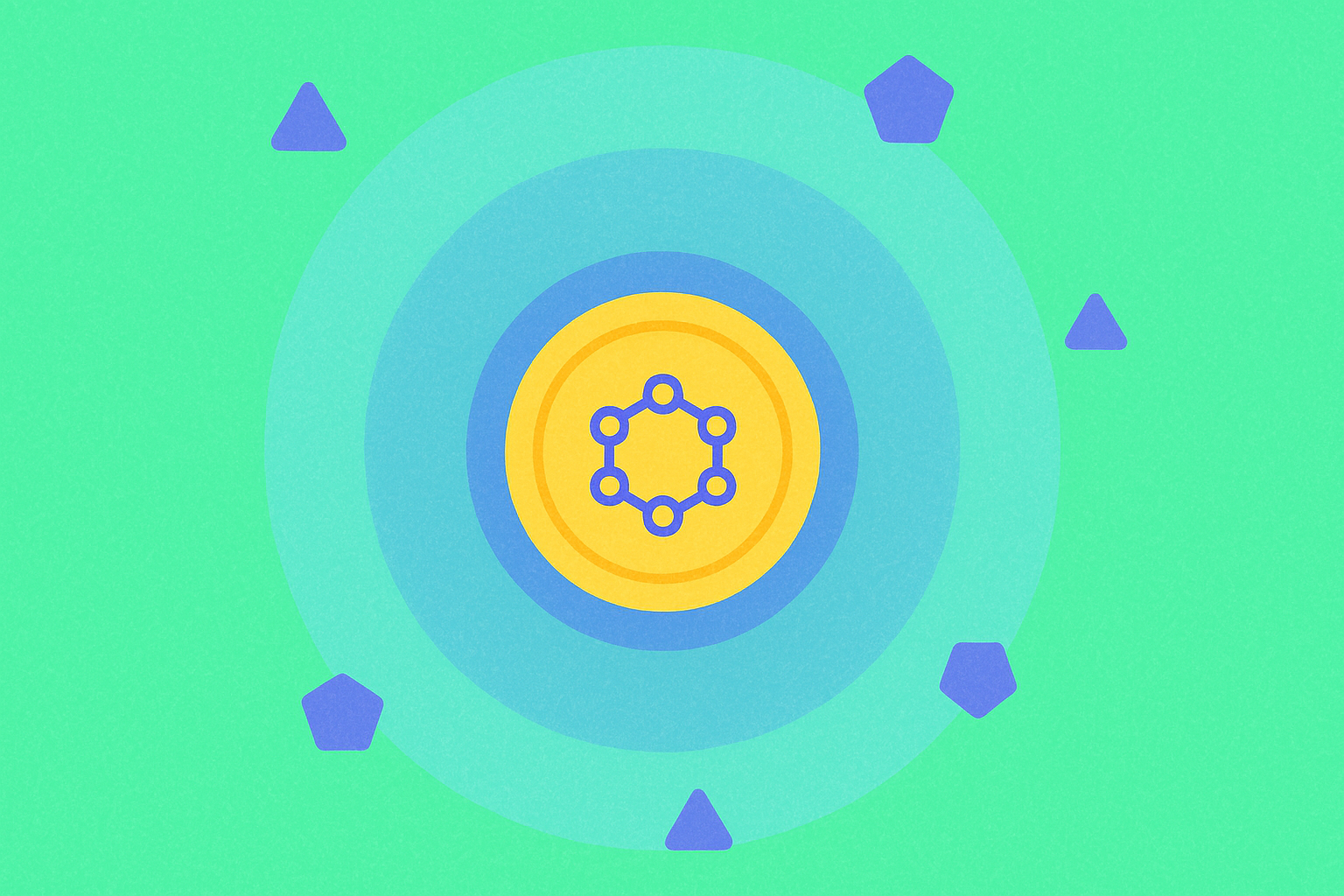
Token Distribution Architecture: Foundation (52.93%), Early Contributors (9.5%), and Investor Allocation (31.57%)
A well-designed token distribution architecture forms the backbone of any cryptocurrency's tokenomics, determining how tokens are allocated among different stakeholder groups. Internet Computer's token distribution model exemplifies this principle through its carefully structured allocation strategy that balances ecosystem development with fair participant incentives.
The Foundation holds the largest share at 52.93% of token allocation, positioning it as the primary stakeholder responsible for protocol development, ecosystem expansion, and long-term network governance. This substantial allocation enables the Foundation to invest in research, infrastructure improvements, and supporting developer communities building on the Internet Computer platform.
Early contributors receive 9.5% of the token supply, reflecting the importance of rewarding those who recognized the project's potential during its inception and contributed to its foundational development. This allocation incentivizes early participation and acknowledges the risk taken by initial supporters who helped establish the network's credibility.
Investor allocation comprises 31.57% of tokens, representing a significant portion dedicated to funding rounds that supported the project's growth. This segment typically includes venture capital, strategic investors, and institutions that provided crucial capital for development and marketing efforts.
Together, these three segments create a balanced tokenomics structure that aligns incentives across different stakeholder groups. The distribution architecture ensures that those contributing resources—whether through governance responsibility, early-stage support, or capital investment—maintain meaningful stakes in the network's success. This approach to token distribution reflects professional tokenomics design that encourages long-term ecosystem development while maintaining decentralized governance principles essential for sustainable blockchain protocols.
Inflation and Deflation Mechanisms: Uncapped Supply Balanced Through Governance and Cycle Burning
ICP operates with a technically uncapped supply that remains balanced through carefully designed inflationary and deflationary mechanisms working in concert. The protocol generates new tokens via two primary inflation channels: governance rewards distributed to neuron holders who participate in decision-making, and node provider rewards compensating entities that operate the network's infrastructure.
These inflationary pressures are systematically offset by deflation mechanisms, most notably cycle burning. When developers deploy smart contracts and pay for computational resources, they convert ICP tokens into cycles—a process that permanently removes tokens from circulation. This burn mechanism creates a direct link between network utility and token scarcity: increased adoption naturally drives more cycle burning, creating deflationary pressure.
Governance plays a crucial role in maintaining this equilibrium. The community can adjust parameters like staking duration requirements and reward rates through proposals, allowing the protocol to respond dynamically to market conditions. Rather than setting a fixed maximum supply cap, this governance-driven approach enables adaptive tokenomics management.
DFINITY's ambitious Mission 70 exemplifies this philosophy—the initiative targets a 70% reduction in inflation by 2026 through coordinated governance decisions affecting both rewards and staking mechanisms. When combined with intensifying cycle burning from expanding onchain adoption, this governance intervention could transition ICP toward genuine deflation, fundamentally reshaping its long-term supply dynamics.
Burn and Utility Design: Converting ICP to Cycles for Reverse Gas Model and Resource Consumption
Internet Computer employs a distinctive reverse gas model that fundamentally ties token burn to computational resource usage. Unlike traditional blockchain systems where users pay gas fees upfront, ICP holders convert their tokens into cycles, which represent computational fuel for canisters operating on the network. The system charges cycles per second based on compute allocation, with a canister requesting full compute resources consuming approximately 10 million cycles per second. This direct linkage between ICP burn and actual resource consumption creates an elegant deflationary mechanism where every computational action permanently removes tokens from circulation.
The utility design extends beyond simple computation through sophisticated resource management protocols. When canisters allocate storage, the system automatically transfers cycles from their main balance into a reserved cycles account to cover future memory costs, preventing inefficient allocations from continuously draining reserves. This memory allocation strategy provides predictability and efficiency. To guard against operational disruptions, developers can implement freezing thresholds that automatically pause canister execution when cycle balances approach critical levels. Alternatively, tools like CycleOps enable automated top-up systems, ensuring uninterrupted service. This architecture demonstrates how tokenomics transcend simple inflation control, becoming integral infrastructure for resource allocation and network sustainability.
Governance Rights and Voting Power: NNS Neurons Enable Staking Rewards and Protocol Decision-Making
The NNS neurons represent a fundamental mechanism through which ICP token holders participate in Internet Computer governance. By staking ICP tokens into neurons, users gain voting rights and the ability to influence protocol decisions. The voting power of each neuron depends on multiple interconnected factors: the quantity of ICP staked, the dissolve delay duration, and the time elapsed since neuron creation. This multi-factor approach ensures that long-term, committed participants wield greater influence over network governance.
Voting participation directly generates staking rewards, creating a virtuous cycle that incentivizes continuous engagement. As neurons accumulate voting maturity through regular participation in governance proposals, stakeholders can either disburse these rewards as additional ICP tokens or reinvest them back into the neuron to compound their voting power. Achieving maximum voting power requires substantial commitment: an eight-year lock-up period combined with four years of maintained holding and consistent voting participation. This design ensures that governance rights remain concentrated among serious, long-term stakeholders rather than short-term speculators, maintaining the integrity of protocol decision-making processes within the Internet Computer ecosystem.
FAQ
What is tokenomics (Tokenomics)? Why is it important for crypto projects?
Tokenomics refers to the economic design of a cryptocurrency, including token supply, distribution, and utility mechanisms. It is crucial for crypto projects because it determines investor confidence, ensures sustainability, affects token value through scarcity, and provides the framework for long-term project success and ecosystem development.
What are the common types of token distribution mechanisms? How to evaluate if a project's token allocation is reasonable?
Common distribution types include private sales, public sales, team reserves, and ecosystem incentives. Evaluate reasonability by assessing distribution transparency, allocation fairness, vesting schedules, and whether incentives align with long-term project development.
What is token inflation mechanism? What risks can excessively high inflation rates bring?
Token inflation mechanism controls supply through new coin issuance. Excessive inflation may cause token depreciation and erode investor confidence. Balanced inflation mechanisms support project sustainability and ecosystem health.
What does token governance mean? How do token holders participate in project decision-making processes?
Token governance grants decision-making power to holders through voting rights. Token holders can propose and vote on project developments, funding allocations, and protocol upgrades. This decentralized model ensures transparency and gives community members direct influence over the project's future direction and operations.
How to analyze whether a project's token economic model is sustainable?
Analyze total supply cap, emission schedule, and demand drivers. Check token distribution fairness, vesting periods, and inflation mechanisms. Sustainable models balance controlled supply growth with strong utility demand and ecosystem incentives.
How does the token burn mechanism affect the long-term value of tokens?
Token burning reduces circulating supply, increasing scarcity and potentially supporting long-term value. However, sustained price appreciation depends on actual project fundamentals and real-world utility. Burning transparency and scale relative to market cap matter more than absolute numbers.
How do vesting schedules and unlock mechanisms impact token price?
Vesting schedules control token supply release over time. Gradual unlocks reduce sudden selling pressure and maintain price stability. Large batch unlocks may cause price dips due to increased supply. Well-designed vesting protects long-term value by preventing rapid dilution and encouraging holder confidence in project sustainability.
What is the tokenomics logic behind liquidity mining and staking rewards?
Liquidity mining and staking rewards incentivize users to provide liquidity and secure the network by earning tokens, enhancing blockchain stability and activity while maintaining token value and network health.

Cryptocurrency Fork Challenges: Understanding Risks and Drawbacks

Understanding Blockchain Forks: Essential Security Practices
DAO: Meaning and Responsibilities

Comprehensive Guide to Cryptocurrency Forks and Blockchain Splits

Understanding Cryptographic Hash Functions for Enhanced Blockchain Security

Understanding Cryptographic Hash Functions: A Comprehensive Guide

How does on-chain data analysis reveal crypto market dynamics with 25% active address growth and $1.2B trading volume?
What is Stellar (XLM)? Analyzing the Whitepaper, Use Cases, and Technical Innovation Behind the Blockchain Payment Network

How does Render (RENDER) community engagement and DApp ecosystem activity compare to other AI infrastructure tokens in 2026?

How does RENDER token price volatility compare to Bitcoin and Ethereum in 2026?

What are the major security risks and smart contract vulnerabilities in Filecoin's history?
