Introduction to Cryptography: A Beginner's Guide

A Short Note on Cryptography
Cryptography stands as one of the fundamental pillars of modern digital security, serving as the mathematical foundation that protects our digital communications and assets. This ancient art of secret writing has evolved into a sophisticated science that underpins everything from secure messaging to blockchain technology.
Understanding Cryptography Fundamentals
When we write a short note on cryptography, it's essential to understand that cryptography is the practice of securing information by transforming it into an unreadable format for unauthorized users. This process involves mathematical algorithms and computational techniques that ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity.
The core purpose of cryptography is to enable secure communication in the presence of adversaries. It protects sensitive information from being accessed, modified, or forged by unauthorized parties, making it indispensable in our interconnected digital world.
Key Components of Cryptographic Systems
To properly write a short note on cryptography, we must explore its essential components:
Encryption and Decryption: The process of converting plaintext into ciphertext (encryption) and reversing it back to plaintext (decryption) forms the backbone of cryptographic systems.
Cryptographic Keys: These are secret values used in conjunction with algorithms to encrypt and decrypt data. The security of cryptographic systems largely depends on key management and protection.
Hash Functions: These one-way mathematical functions convert data of any size into a fixed-size output, crucial for data integrity verification and password storage.
Digital Signatures: These provide authentication and non-repudiation, ensuring that messages genuinely originate from claimed senders.
Types of Cryptography
Symmetric Cryptography
Symmetric cryptography uses the same key for both encryption and decryption. This method is fast and efficient for processing large amounts of data. Common algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard). The main challenge lies in securely sharing the key between parties.
Asymmetric Cryptography
Also known as public-key cryptography, this system uses a pair of keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. RSA and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) are prominent examples. This approach solves the key distribution problem inherent in symmetric systems.
Hash Functions
Cryptographic hash functions like SHA-256 and SHA-3 create unique digital fingerprints of data. These are extensively used in blockchain technology, password storage, and data integrity verification.
Applications in Modern Technology
When we write a short note on cryptography and its applications, the scope is remarkably broad:
Secure Communications: Cryptography protects emails, instant messages, and voice calls through end-to-end encryption protocols.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency: Digital currencies rely heavily on cryptographic principles for transaction security, wallet protection, and consensus mechanisms. Major trading platforms implement robust cryptographic protocols to secure user assets and transactions.
E-commerce and Banking: Online transactions depend on SSL/TLS certificates and cryptographic protocols to protect financial information.
Digital Identity: Cryptography enables secure authentication systems, digital signatures, and identity verification processes.
Cryptography in Blockchain Technology
The cryptocurrency ecosystem demonstrates cryptography's critical importance. Blockchain networks utilize multiple cryptographic techniques:
- Public-key cryptography for wallet addresses and transaction authorization
- Hash functions for block linking and mining processes
- Digital signatures for transaction verification and ownership proof
- Merkle trees for efficient transaction verification
These cryptographic foundations ensure that digital assets remain secure across decentralized networks, whether traded on centralized platforms or peer-to-peer networks.
Contemporary Challenges
As we write a short note on cryptography's current landscape, several challenges emerge:
Quantum Computing Threat: Future quantum computers may break current cryptographic algorithms, prompting development of quantum-resistant cryptography.
Key Management: Securely storing and managing cryptographic keys remains a significant challenge, especially in cryptocurrency contexts where lost keys mean permanent asset loss.
Implementation Vulnerabilities: Even strong cryptographic algorithms can be compromised through poor implementation or side-channel attacks.
Regulatory Balance: Governments worldwide struggle to balance security needs with privacy rights, creating complex regulatory environments.
Future Directions
The future of cryptography includes:
Post-Quantum Cryptography: Development of algorithms resistant to quantum computer attacks is accelerating, with standardization efforts underway.
Homomorphic Encryption: This allows computations on encrypted data without decryption, enabling privacy-preserving cloud computing.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: These cryptographic protocols allow verification of information without revealing the information itself, increasingly important for privacy-focused applications.
Lightweight Cryptography: As IoT devices proliferate, efficient cryptographic solutions for resource-constrained devices become crucial.
Conclusion
To write a short note on cryptography is to capture the essence of digital security itself. Cryptography has evolved from ancient cipher methods to sophisticated mathematical systems that protect our digital lives. Its applications span from securing personal communications to enabling global financial systems and blockchain networks.
Understanding cryptography's principles, methods, and applications is increasingly important as our world becomes more digitally interconnected. Whether protecting personal data, securing financial transactions, or enabling decentralized technologies, cryptography remains the cornerstone of digital trust and security. As technology advances and new threats emerge, cryptography continues to evolve, ensuring that our digital future remains secure and private.
The ongoing development in cryptographic research and implementation demonstrates its vital role in shaping a secure digital ecosystem for generations to come.
FAQ
What are the four types of cryptography?
The four main types are symmetric key cryptography, asymmetric key cryptography, hash functions, and stream encryption. Symmetric uses one key, asymmetric uses public-private key pairs, hash functions create fixed-length outputs, and stream encryption encrypts data sequentially.
What is cryptology in simple words?
Cryptology is the science of securing information through encryption and decryption. It protects data from unauthorized access by converting readable information into coded form that only authorized users can decode and understand.
What are some examples of cryptography?
Common examples include RSA encryption for secure communications, AES for data protection, and SHA-256 hashing used in blockchain technology. These methods encrypt sensitive information through complex mathematical algorithms.
How to explain cryptography to a child?
Cryptography is like a secret code that keeps messages safe. It changes words into secret codes that only people with the key can understand. This helps protect personal information online.

Cryptography: From Ancient Ciphers to Blockchain. The Complete Guide to Information Security in the Digital Age

Understanding Merkle Proofs in Blockchain Technology
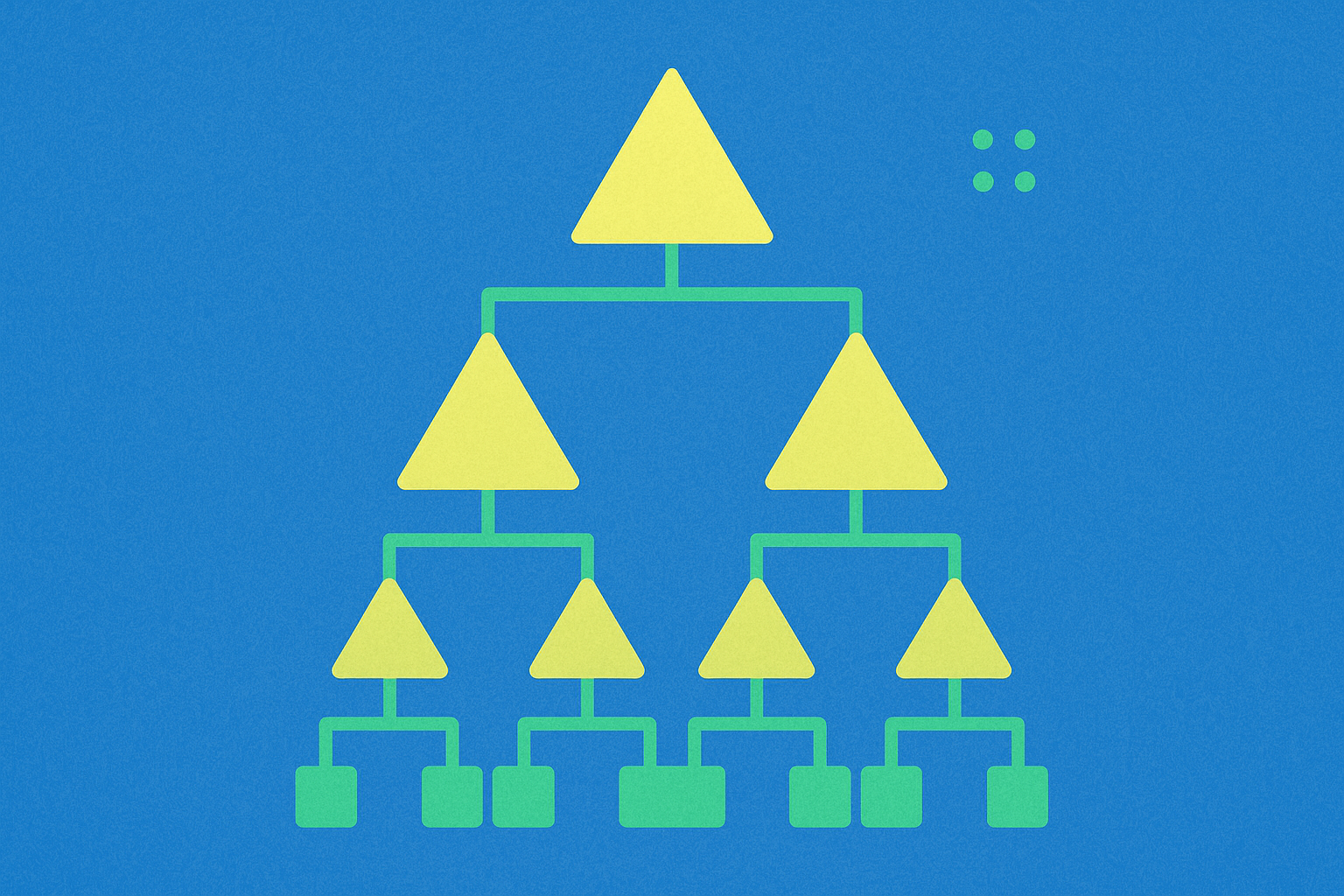

Understanding Merkle Tree Proofs in Blockchain Technology

Understanding Cryptography: Essential Concepts for Blockchain Security
Understanding Merkle Proofs in Blockchain Technology

Enhancing Security in Blockchain Networks with Cryptography Techniques
What is Fuel Network (FUEL)? Everything You Need to Know about FUEL

What Is BNB Chain?

All You Need To Know About Yescoin

How to Buy Baron ($BARRON) Coin: What is Baron Trump Cryptocurrency?

What Is AI Dev Agent (AIDEV)? No-Code Platform for Building Products