Introduction to Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAG)


What Is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)?
A directed acyclic graph, or DAG, is a data modeling structure that some cryptocurrencies use instead of blockchain. This technology has emerged as a compelling alternative in the crypto space, offering distinct advantages over traditional blockchain systems.
DAG vs. Blockchain Technology
While blockchain technology has long dominated the cryptocurrency industry, DAG offers an alternative that may address some of blockchain’s inherent limitations.
DAG Architecture
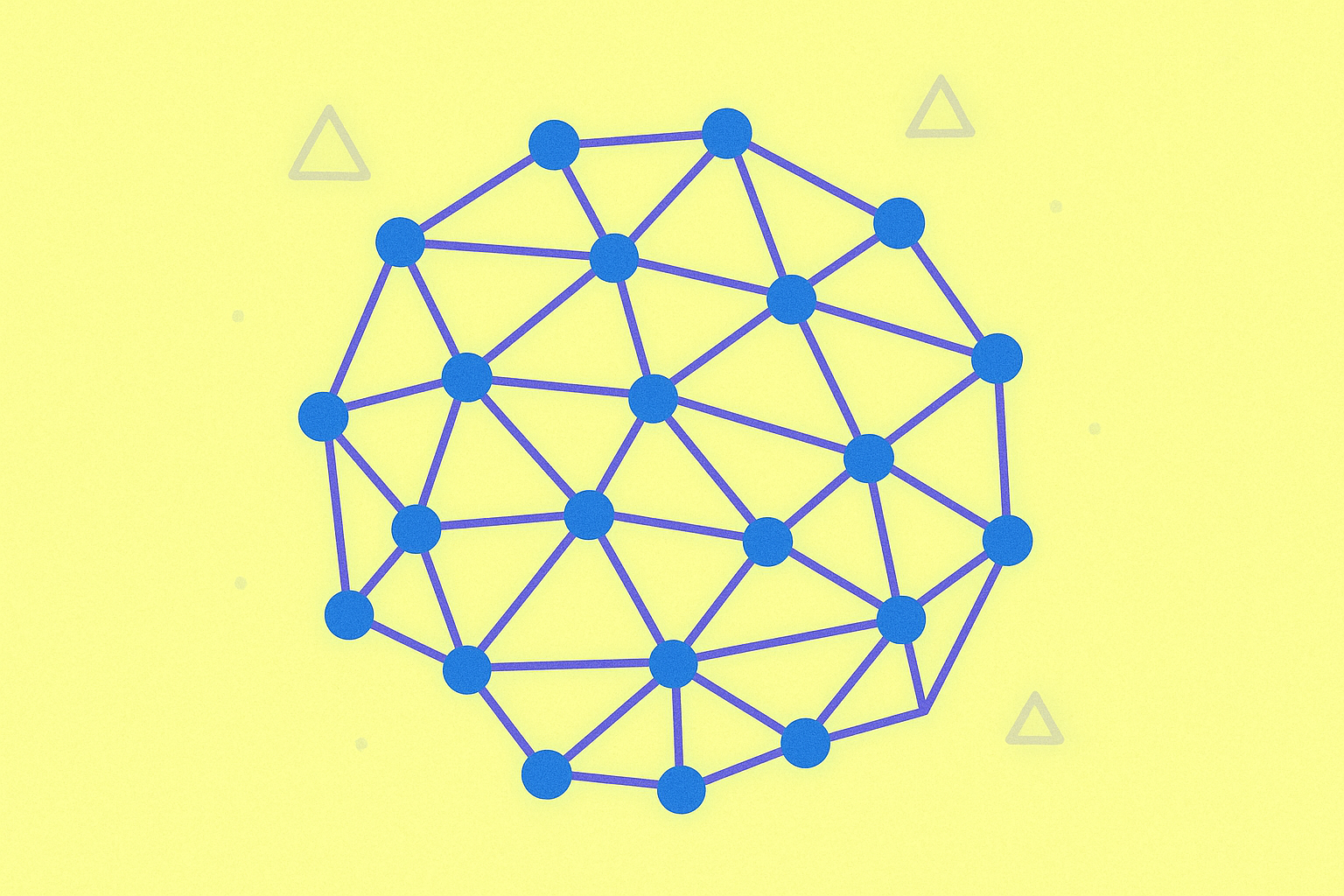
DAG architecture is built around circles and lines. Each circle (vertex) represents activities to be added to the network, while each line (edge) marks the order in which transactions are approved. These lines move only in one direction, which is why the structure is called a directed acyclic graph.
What Is the Difference Between a DAG and a Blockchain?
The main difference is that DAGs do not create blocks as blockchains do. Instead, transactions are stacked upon each other, which dramatically increases transaction speed compared to traditional blockchain models.
How Does DAG Technology Work?
In a DAG-based system, a user must confirm a previous transaction to submit a new one. Unconfirmed transactions are known as "tips." This process forms successive transaction layers, allowing the network to scale efficiently.
What Is DAG Used For?
DAGs are mainly used to process transactions more efficiently than blockchains. They are particularly effective for micropayments, thanks to their low or zero transaction fees. Additionally, they are energy efficient since they do not depend on traditional mining processes.
Which Cryptocurrencies Use DAG?
Examples of cryptocurrencies that leverage DAG technology include:
- IOTA (MIOTA): Renowned for fast transactions, scalability, and security.
- Nano: Combines DAG and blockchain to deliver instant, feeless transactions.
- BlockDAG: Applies DAG for energy-efficient mining solutions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DAG
Advantages:
- Speed: Not constrained by block times.
- Low or zero transaction fees: Ideal for microtransactions.
- No mining required: Lower energy consumption.
- Scalability: Avoids the scalability challenges seen with blockchains.
Disadvantages:
- Decentralization concerns: Some DAG protocols feature centralized components.
- Limited large-scale testing: Adoption is not yet as widespread as other blockchain-based technologies.
Conclusion
Directed acyclic graphs are an emerging technology in the cryptocurrency sector. While they offer clear benefits in speed, scalability, and energy efficiency, they are still evolving. DAGs show strong potential for specialized uses, such as micropayments and fast transactions, but have yet to prove they can fully replace blockchain technology. The future role of DAGs in the crypto ecosystem will depend on how the technology advances and how current challenges are addressed in the years ahead.
FAQ
What Does DAG Stand For?
DAG stands for Directed Acyclic Graph—a data structure used by some cryptocurrencies as an alternative to traditional blockchain systems.
What Is a DAG? Example Included
In cryptocurrencies, a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a structure that enables parallel transactions. For instance, IOTA uses a DAG called the Tangle to process multiple transactions at once, increasing both speed and scalability.
What Is the Purpose of a DAG?
DAG technology enhances the scalability and speed of crypto transactions by allowing parallel processing and eliminating the need for conventional mining.
What Is DAG?
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a data structure used in select cryptocurrencies to improve transaction speed and scalability, providing an alternative to traditional blockchain technology.

Guide to Engaging in Parachain Auctions on Polkadot

Understanding Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)

Mastering the Fundamentals of Directed Acyclic Graphs

Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs in Blockchain Technology

Exploring the Potential of Internet Computer Protocol (ICP)
Exploring Distributed Ledgers: A Non-Block Approach

Understanding Decentralized Exchanges and DEX Aggregators
DEX Aggregator Platform Upgrade: Enhanced Trading Experience

Comprehensive Multi-Chain NFT Marketplace

What Is Monad? How to Claim Monad (MON) Tokens Using the Web3 Faucet

Grok AI Adoption: Ushering in a New Era for Blockchain Applications
